Starting a business can be one of the most rewarding endeavors. However, it also requires meticulous planning, execution, and a clear understanding of both the market and internal operations. Therefore, this business startup guide offers a comprehensive overview of each stage, from initial idealization to launch. Additionally, it highlights best practices and focuses on key areas essential for long-term success. Begin with this business startup guide to get grounded. Then, consider scheduling a consultation with a business consultant for expert input. Furthermore, take a course or read a business book to expand your knowledge.
The journey from a business idea to a successful startup is both exciting and demanding. However, turning a concept into reality involves more than just passion. Entrepreneurs must navigate multiple steps, from defining the business model to handling daily operations. Additionally, each phase requires thoughtful planning and effective execution. Therefore, paying attention to each stage can help your startup stand out and grow in a competitive market.
Starting a business involves various components, including market research, business planning, legal structuring, financial management, product development, marketing, and team management. This comprehensive business startup guide aims to provide aspiring entrepreneurs with a roadmap to navigate these areas effectively.
Idealization and Market Research
Idealization
The first step in starting a business is developing a viable business idea. Ideally, this idea should address a specific problem or meet a particular need in the market. Therefore, it’s important to begin with careful observation and analysis.
Identifying a Problem: Start by looking for gaps in the market or challenges that consumers frequently encounter. Additionally, pay attention to pain points in existing products or services. Your business idea should aim to solve these problems in a practical and valuable way.
Brainstorming Ideas: Once you’ve identified a potential issue, use creative tools such as mind mapping, group brainstorming, and SWOT analysis to generate ideas. Furthermore, compare and evaluate each idea to identify the most promising ones. These exercises not only inspire new concepts but also reveal potential risks and advantages.
Validation: Before moving forward with business planning, take time to validate your idea. Therefore, seek feedback from potential customers, industry professionals, and trusted mentors. Additionally, consider testing your concept through informal surveys or pilot offers to gather real-world input.
Best Practices:
To support this stage, consider maintaining an idea journal to track and refine your thoughts over time. Additionally, engage with potential customers early to gain insight into their expectations and frustrations. Moreover, remain flexible and willing to adjust your idea based on feedback and evolving market needs. These steps will help you build a stronger foundation before committing time and resources to development.
Market Research
Conducting thorough market research is essential to understanding your target audience, market size, competition, and industry trends. Therefore, it plays a key role in shaping your overall strategy. Additionally, it allows you to make informed decisions based on real data rather than assumptions. For this reason, it is a central part of this business startup guide.
Target Audience: Begin by identifying your ideal customers, including their demographics, interests, and buying behaviors. Additionally, consider what problems they face and how your product or service can help solve them.
Market Size and Growth: Next, assess the total market size and evaluate growth trends. This helps determine if there is enough demand to support your business. Furthermore, understanding growth potential can guide your planning and future expansion.
Competitive Analysis: Study your competitors closely to learn about their strengths, weaknesses, and market positions. Additionally, review their pricing, branding, and customer feedback to see how you can differentiate your offering.
Industry Trends: Stay updated on industry developments and emerging technologies that may impact your business. Therefore, read trade publications, attend events, and follow thought leaders in your field. This helps you stay ahead of change and make better strategic choices.
Best Practices: To gain deeper insights, use both primary methods (such as surveys and interviews) and secondary sources (including market reports and online data). Additionally, create detailed customer personas to better understand your audience. Moreover, revisit your research regularly to adapt to shifts in consumer behavior or market conditions. This ongoing process helps keep your strategy aligned with real-world trends.
Business Planning
Creating a Business Plan
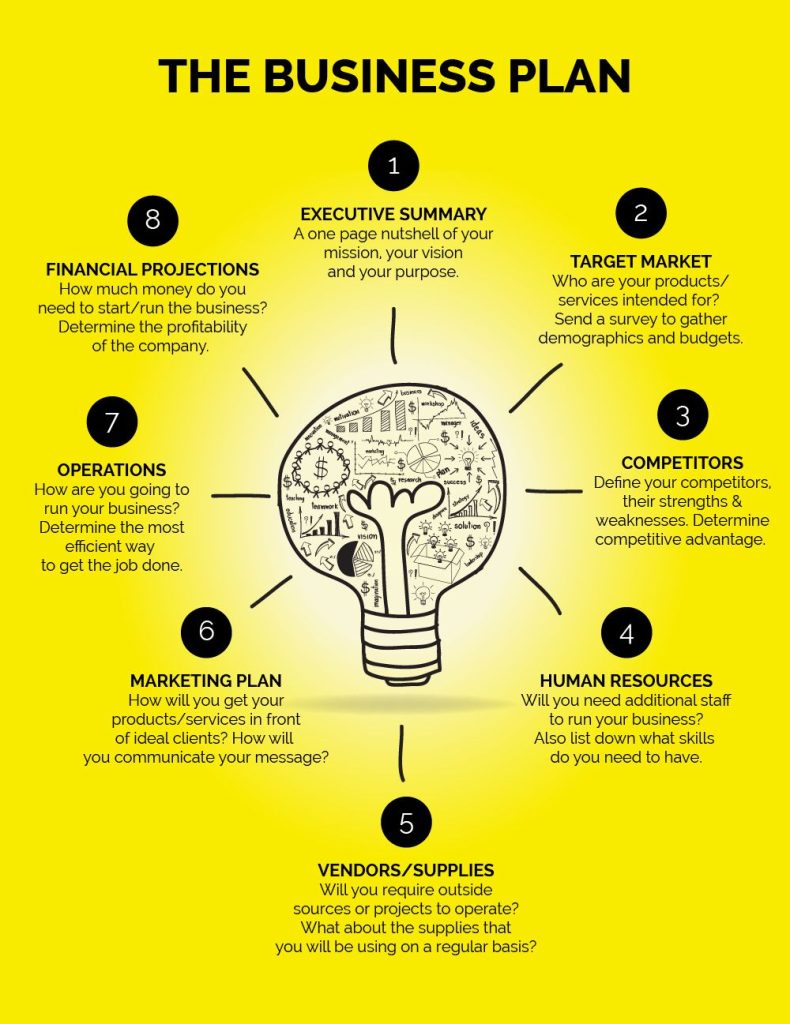
A comprehensive business plan serves as a roadmap for your startup, clearly outlining your goals, strategies, and financial projections. Therefore, it helps you stay focused and organized as your business grows. Additionally, it provides a useful tool when seeking funding or partnerships.
Executive Summary: Begin with a high-level overview of your business. Include your mission statement, vision, and key objectives. Additionally, highlight what sets your business apart from others in the market.
Business Description: Describe your business in more detail, including the products or services you offer. Therefore, be clear about your unique value proposition and the specific market you aim to serve.
Market Strategy: Outline your marketing and sales strategy, including how you plan to attract and retain customers. Additionally, describe your pricing model and promotional efforts to show how you intend to reach your audience.
Operational Plan: Explain the day-to-day operations of your business. Include production processes, supply chain management, and logistics. Therefore, give readers a full picture of how your business will function.
Financial Plan: Present financial projections, funding needs, and a detailed budget. Additionally, use charts or tables to clarify your assumptions and goals. This section helps demonstrate long-term sustainability and preparedness.
Best Practices:
Keep your plan concise and focused, typically no more than 20 to 30 pages. Additionally, use reliable data to support your assumptions and projections. Moreover, review and update your business plan regularly to adjust for changes in the market or your performance. This keeps your strategy relevant and actionable.
Setting SMART Goals
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals helps focus your efforts and track progress.
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish criteria to measure your progress.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals that are attainable.
- Relevant: Ensure goals align with your overall business objectives.
- Time-bound: Set deadlines for achieving your goals.
Best Practices:
- Break down long-term goals into smaller, actionable steps.
- Use tools like OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) to align team efforts.
- Regularly review and adjust goals based on performance and feedback.
Legal and Structural Setup
Choosing a Business Structure
Selecting the right business structure is an important decision, as it affects your legal responsibilities, tax obligations, and personal liability. Therefore, no business startup guide would be complete without this step. Additionally, your chosen structure can influence how your business operates and grows over time.
Sole Proprietorship: This is the simplest structure, with the owner maintaining full control. However, the owner also bears full personal liability for business debts. Therefore, this option is best suited for low-risk ventures or individuals starting alone.
Partnership: This structure involves two or more individuals who share ownership, profits, and responsibilities. Additionally, each partner is personally liable for business obligations. Therefore, it is important to establish a clear agreement to avoid misunderstandings.
Limited Liability Company (LLC): This option provides liability protection while allowing profits to be taxed at the owner’s personal income rate. Additionally, it offers flexibility in management and fewer formalities than a corporation. Therefore, it is a popular choice for small to mid-sized businesses.
Corporation: A more complex structure, a corporation offers strong liability protection and the ability to raise capital through stock. However, corporations face double taxation, with taxes applied at both the corporate and personal level. Therefore, it’s often selected by larger businesses with long-term scaling plans.
Best Practices:
Consult with a legal or financial advisor to weigh your options. Additionally, consider liability, tax treatment, and administrative duties. Moreover, choose a structure that supports your business goals both now and in the future. Careful planning at this stage can save time and reduce complications later.
Registering Your Business
Once you choose a business structure, register your business with the appropriate government authorities.
- Business Name Registration: Ensure your business name is unique and register it with your state or local government.
- EIN: Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS for tax purposes.
- Licenses and Permits: Identify and obtain the necessary licenses and permits required for your industry and location.
Best Practices:
- Use online resources like the SBA (Small Business Administration) to identify required registrations and permits.
- Keep all legal documents and registrations organized and accessible.
- Regularly review and renew licenses and permits to remain compliant.
Intellectual Property Protection
Protecting your intellectual property (IP) is crucial to safeguard your business assets and competitive advantage.
- Trademarks: Register trademarks for your business name, logo, and slogans to protect your brand identity.
- Patents: Apply for patents to protect inventions and proprietary processes.
- Copyrights: Protect original works of authorship, such as written content, software, and designs, through copyrights.
Best Practices:
- Conduct thorough searches to ensure your IP is unique and not infringing on existing rights.
- Work with an IP attorney to navigate the application process.
- Regularly monitor and enforce your IP rights to prevent unauthorized use.
Financial Planning and Funding
Budgeting and Financial Projections
Effective financial planning involves creating a detailed budget and financial projections to manage expenses and forecast revenue. Understanding money requirements is critical and part of this business startup guide.
- Startup Costs: Identify and estimate initial startup costs, including equipment, inventory, marketing, and legal fees.
- Operating Budget: Develop an operating budget to manage ongoing expenses such as rent, utilities, payroll, and marketing.
- Financial Projections: Create financial projections, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets, to forecast future financial performance.
Best Practices:
- Use accounting software to streamline budgeting and financial tracking.
- Regularly review and adjust your budget based on actual performance.
- Seek advice from financial advisors or accountants for accurate financial planning.
Securing Funding
Raising capital is essential for starting and growing your business. Explore various funding options to secure the necessary financial resources.
- Personal Savings: Use personal savings or contributions from family and friends to fund initial startup costs.
- Angel Investors: Seek funding from angel investors who provide capital in exchange for equity ownership.
- Venture Capital: Attract venture capital firms that invest in high-growth startups with significant potential.
- Crowdfunding: Use crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo to raise small amounts of capital from a large number of people.
- Bank Loans: Apply for business loans from banks or credit unions to finance your operations.
- Grants and Programs: Explore government grants, loans, and support programs for small businesses.
Best Practices:
- Prepare a compelling business plan and pitch to attract investors or secure loans.
- Evaluate the pros and cons of each funding option to choose the best fit for your business.
- Maintain good financial health and creditworthiness to improve your chances of securing funding.
Financial Management
Effective financial management ensures the business remains financially healthy and sustainable.
- Bookkeeping: Maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records of all transactions.
- Accounting: Prepare financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Cash Flow Management: Monitor cash flow to ensure the business can meet its financial obligations.
Best Practices:
- Use accounting software to streamline financial management and reporting.
- Regularly review financial statements to assess performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Work with a professional accountant or financial advisor for complex financial tasks.
Product Development and Operations
Developing Your Product or Service
Product development involves creating and refining your product or service to meet customer needs and market demands.
- Prototyping: Develop prototypes to test and validate your product or service.
- Testing: Conduct rigorous testing to ensure quality, functionality, and usability.
- Iteration: Use feedback from testing and customers to refine and improve your product or service.
Best Practices:
- Involve customers in the development process to ensure the product meets their needs.
- Use agile development methodologies to iterate quickly and efficiently.
- Regularly update and enhance your product or service based on market feedback.
Operations Management
Efficient operations are essential for delivering products or services to customers effectively and cost-efficiently.
- Supply Chain Management: Manage suppliers, inventory, and logistics to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
- Quality Control: Implement quality control processes to maintain high standards and meet customer expectations.
- Process Improvement: Continuously identify and eliminate inefficiencies in workflows and systems.
Best Practices:
- Use inventory management software to track stock levels and forecast demand.
- Implement lean practices such as continuous improvement (Kaizen) and waste reduction.
- Regularly review and update operational processes to adapt to changing business needs and technologies.
Technology Integration
Integrating technology into your business operations can enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
- Business Software: Use software solutions for tasks such as accounting, project management, customer relationship management (CRM), and human resources.
- Data Analytics: Implement data analytics tools to gain insights into business performance and inform decision-making.
- Automation: Use automation tools and technologies to reduce manual tasks and improve accuracy.
Best Practices:
- Evaluate and select technology solutions that align with business needs and goals.
- Train employees to effectively use technology and stay updated with new tools and trends.
- Regularly review and upgrade technology to maintain competitiveness and efficiency.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Building a Strong Brand
A strong brand identity sets your business apart from competitors and creates a memorable impression on customers.
- Brand Positioning: Define how the brand is perceived in the market and what makes it unique.
- Brand Messaging: Craft clear and consistent messages that communicate the brand’s value proposition.
- Visual Identity: Create a cohesive visual identity, including logos, colors, fonts, and design elements.
Best Practices:
- Conduct market research to understand customer perceptions and preferences.
- Develop brand guidelines to ensure consistency across all marketing materials and channels.
- Regularly review and update the brand identity to reflect changes in the market and business.
Implementing a Multi-Channel Marketing Strategy
A multi-channel marketing strategy leverages various online and offline channels to reach and engage customers.
- Digital Marketing: Utilize digital channels such as social media, email marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable and relevant content to attract and retain customers (e.g., blog posts, videos, infographics).
- Traditional Marketing: Incorporate traditional channels such as print advertising, direct mail, and events.
Best Practices:
- Identify the most effective channels for reaching the target audience.
- Develop a content calendar and marketing plan to ensure consistent and timely execution.
- Use analytics and tracking tools to measure the effectiveness of each channel and campaign.
Sales Strategy
A strong sales strategy focuses on customer acquisition, retention, and growth.
- Sales Funnel: Develop a sales funnel to guide prospects through the buying process, from awareness to conversion.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Implement a CRM system to manage customer interactions, track sales activities, and improve customer relationships.
- Sales Training: Provide ongoing training and development for the sales team to enhance their skills and performance.
Best Practices:
- Use data and analytics to identify high-potential leads and target them effectively.
- Develop personalized sales approaches to meet the needs and preferences of different customer segments.
- Regularly review and refine the sales strategy based on performance and feedback.
Customer Engagement and Retention
Building strong relationships with customers is essential for driving repeat business and long-term success.
- Customer Support: Provide responsive and helpful customer support through various channels (e.g., phone, email, chat).
- Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty programs to reward repeat customers and encourage referrals.
- Feedback and Improvement: Collect and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance the customer experience.
Best Practices:
- Use customer surveys and feedback tools to gather insights into customer satisfaction.
- Personalize interactions and offers to create a more engaging and meaningful customer experience.
- Address customer issues and concerns promptly to maintain trust and loyalty.
Team Building and Management
Hiring the Right People
Building a talented and motivated team is essential for business success.
- Job Descriptions: Create clear and detailed job descriptions that outline the roles and responsibilities of each position.
- Recruitment Strategies: Use effective recruitment strategies to attract top talent, including job postings, referrals, and recruitment agencies.
- Interview Process: Conduct structured interviews and use assessment tools to evaluate candidates.
Best Practices:
- Focus on cultural fit as well as skills and experience.
- Provide competitive compensation and benefits to attract and retain top talent.
- Use onboarding programs to help new hires integrate into the team and understand the company culture.
Developing Your Team
Investing in employee development enhances skills, motivation, and performance.
- Training Programs: Provide ongoing training and development opportunities to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
- Career Development: Develop individualized development plans and career paths for employees.
- Performance Management: Implement performance management systems to set goals, provide feedback, and evaluate performance.
Best Practices:
- Use a mix of training methods, including workshops, online courses, and on-the-job training.
- Encourage employees to pursue certifications and professional development opportunities.
- Recognize and reward high performers to motivate and retain top talent.
Fostering a Positive Company Culture
A positive company culture enhances employee satisfaction, productivity, and retention.
- Values and Beliefs: Clearly define and communicate the company’s core values and beliefs.
- Work Environment: Create a supportive and inclusive work environment that promotes well-being and work-life balance.
- Team Building: Organize team-building activities and events to strengthen relationships and collaboration.
Best Practices:
- Lead by example and demonstrate the values and behaviors expected of employees.
- Provide regular feedback and recognition to reinforce positive behaviors.
- Address conflicts and issues promptly to maintain a healthy and positive work environment.
Leadership and Management
Effective leadership and management are crucial for guiding the business and motivating the team.
- Visionary Leadership: Clearly communicate the vision and mission of the business to inspire and guide employees.
- Empowerment: Empower employees by delegating authority and providing opportunities for growth and development.
- Decision-Making: Make informed and timely decisions that align with the business’s strategic goals.
Best Practices:
- Develop leadership skills through training, mentorship, and continuous learning.
- Foster a culture of transparency, accountability, and collaboration.
- Regularly seek feedback from employees and stakeholders to improve leadership effectiveness.
Starting a business involves a multitude of steps and considerations. From idea development and market research to legal setup, financial planning, product development, marketing, and team management, each phase plays a key role. Therefore, it is important to approach every stage with focus and strategy. Additionally, by applying best practices across these areas, entrepreneurs can build a strong foundation for their business. As a result, they are better prepared to face the challenges of the marketplace with confidence. We hope this business startup guide has offered helpful support along the way.
Success in business also requires ongoing learning, regular adaptation, and continuous improvement. Therefore, staying committed to excellence and consistently applying proven strategies is essential. Additionally, embracing change and remaining flexible can increase long-term sustainability. This comprehensive business startup guide not only outlines the key steps but also provides a clear roadmap for starting and growing a successful business. Furthermore, it equips you with practical knowledge and tools needed to pursue your entrepreneurial goals with confidence and clarity. If you require additional assistance, try our online business courses, books, or our business startup consulting services. We look forward to help.