Running a business means making decisions that affect your pricing, products, and timing. Conducting a supply and demand analysis helps you make those decisions with more clarity. It shows you what buyers want and how much of it is available. That gives you the information you need to plan with confidence.
Running a business means making decisions that affect your pricing, products, and timing. Conducting a supply and demand analysis helps you make those decisions with more clarity. It shows you what buyers want and how much of it is available. That gives you the information you need to plan with confidence.
Additionally, supply and demand influence nearly every market outcome. If you ignore them, you risk overpricing, understocking, or missing sales opportunities. Therefore, understanding how these forces work can make a noticeable difference in your results. You stop relying on opinions and start relying on market behavior.
However, getting reliable insight takes more than watching a few numbers. You need to track trends, study changes, and compare patterns over time. That means combining hard data with customer feedback. It also means checking your assumptions before you act. Therefore, your analysis becomes a regular tool, not a one-time review.
You don’t need complex systems to get started. You only need a consistent method for gathering and reviewing key data. Additionally, you need to apply that data to your decisions. When you do that, your actions reflect real demand, not guesses. That approach helps you stay ready instead of scrambling later.
The better you understand supply and demand, the stronger your strategy becomes. You start to see where your business fits and where it can grow. Therefore, learning this process now pays off over time.
Understanding the Basics of Supply and Demand
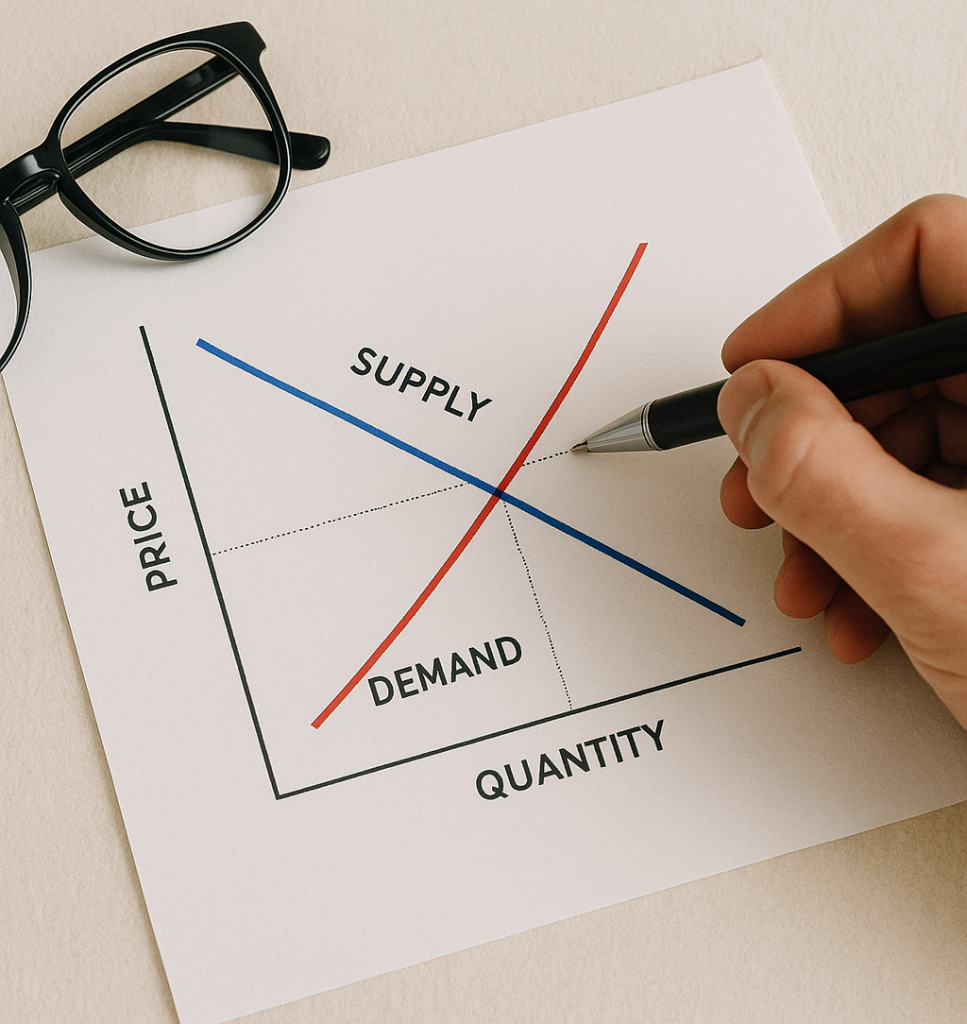
Supply and demand are the two forces that shape how markets work. Supply refers to how much of a product sellers offer. Demand is the amount that buyers want to purchase. When these forces meet, they form an equilibrium. That’s the point where supply equals demand, and the price tends to stabilize.
However, markets are rarely static. Prices shift when either supply or demand changes. For example, if demand increases but supply remains the same, prices tend to rise. On the other hand, if supply increases while demand stays steady, prices often fall. Therefore, understanding this balance helps you make better business decisions.
Additionally, price elasticity affects how sensitive buyers are to price changes. Some products are elastic, meaning demand drops if prices rise. Others are inelastic, where demand stays steady despite price shifts. This concept matters when setting prices or planning production.
When you study these patterns, you start seeing how each part connects. Conducting a supply and demand analysis helps you understand why customers behave the way they do. It also helps you decide how much to produce, when to enter a market, or whether to raise prices.
Therefore, getting familiar with these basics gives you a strong foundation. Your strategy becomes more focused when you know how supply and demand interact. Instead of guessing, you rely on market signals to guide your choices. That’s what makes this analysis such a practical part of business planning.
Identifying Key Market Factors
When you examine supply and demand, you need to understand what drives them. These drivers include both internal and external factors. Internal factors usually come from within your business, while external ones come from the market or environment around you.
Consumer preferences are one of the biggest influences. When customer tastes change, demand moves with them. For example, if people shift toward healthier products, demand for certain foods will increase. Therefore, tracking trends helps you stay aligned with what buyers actually want.
Additionally, production costs can affect how much you supply. If raw materials get more expensive, your ability to offer products at the same price changes. That shift impacts supply even if demand stays constant. Therefore, watching input costs is part of staying ready.
You should also keep an eye on competition. When more players enter a market, supply usually increases. That added supply can push prices lower. However, competition can also influence demand by shaping customer expectations or introducing new features.
Economic conditions also matter. Interest rates, inflation, and employment levels all influence how much people spend and what they buy. If people feel confident, demand often grows. If they feel uncertain, demand may shrink. Therefore, broad market data helps complete your picture.
Conducting a supply and demand analysis requires you to connect these different forces. You’re not only looking at numbers but also the reasons behind them. With this view, your decisions become more informed and better timed.
Collecting and Analyzing Market Data
To make smart business decisions, you need accurate data. That includes both quantitative and qualitative information about your market. Quantitative data gives you numbers, such as sales figures or pricing trends. Qualitative data shows what customers think or how they behave.
You can start by using market research reports. These often contain sales volumes, industry growth rates, and competitor benchmarks. Therefore, they help you see where your business fits in the market. Additionally, these reports give context for changes in supply and demand.
Customer surveys offer direct feedback. You can learn why people buy, what they value, and how much they are willing to spend. This type of insight often points to future demand shifts. Therefore, surveys support decisions around product development and pricing.
You should also look at industry databases. These include trade data, production volumes, and market forecasts. By reviewing this information, you get a better sense of overall supply conditions. However, you’ll need to combine sources for a clearer picture.
Additionally, analyzing the data is as important as collecting it. Look for trends and patterns over time. Compare seasonal highs and lows or shifts in customer behavior. These patterns help you understand what drives your market.
Conducting a supply and demand analysis depends on this step. Without good data, you’re guessing. With it, your decisions become grounded and timely. Therefore, gathering and reviewing market data should be a regular part of your business planning.
Evaluating Demand Trends and Forecasting Needs
Understanding what drives demand begins with spotting patterns in customer behavior. These patterns show up in sales data, website traffic, or repeat purchases. When you monitor these trends regularly, you start to see where interest is growing or fading.
Additionally, demand often shifts with seasons, trends, or new technology. Therefore, reviewing past performance by quarter or year can help you find repeat patterns. If sales peak every summer, you can plan ahead. However, short-term spikes may signal a different kind of trend, such as a social media surge or new competitor.
You can also use forecasting tools to estimate what comes next. Moving averages, regression models, and industry benchmarks offer practical ways to make projections. While no method is perfect, using multiple models gives you more stable results. Therefore, forecasting becomes less about guessing and more about planning.
Customer feedback also plays a part. What people say about pricing, features, or availability can hint at future buying decisions. Therefore, pair your numbers with direct input from your audience. This balance helps you understand both what people do and why they do it.
Conducting a supply and demand analysis without trend data is incomplete. Your decisions need to reflect not just current demand but where demand is headed. That way, you avoid missed sales or overstock problems. Additionally, forecasting helps you react before shifts happen, not after.
Assessing Supply Chain Capacity and Constraints
Meeting customer demand depends on how well your supply chain performs. You need enough inventory, fast production, and reliable logistics. If any part fails, your ability to meet demand weakens. Therefore, assessing capacity helps you avoid shortages, delays, or missed sales.
Start by looking at your suppliers. Can they deliver what you need, when you need it? If they face disruptions, so do you. Additionally, having more than one supplier lowers risk. That gives you flexibility when things change.
Production lead times also matter. If it takes weeks to make your product, you must plan ahead. Therefore, accurate forecasting ties directly into how you manage supply. A delay in production affects every part of your operation.
Inventory levels should match expected demand, not guesswork. Too much ties up cash. Too little leads to lost sales. However, using tools like reorder points and safety stock levels can help. These keep your inventory balanced without relying on luck.
Logistics is another part of the equation. You need to move products from warehouse to customer on time. If shipping takes too long, customers notice. Therefore, review your delivery systems and carrier performance often.
Conducting a supply and demand analysis without studying supply capacity leaves gaps in your planning. You need both sides to get a complete picture. When you know your limits, you can make smarter decisions. Additionally, you’ll reduce surprises and react faster when conditions change.
Applying Analysis to Strategic Decisions
Understanding supply and demand gives you more than insight. It helps you make better decisions across many parts of your business. When you know how customers behave and how supply shifts, your strategy becomes clearer and more focused.
Pricing is often the first area where this knowledge matters. If demand rises and supply stays low, you may raise prices. However, if competition increases and supply expands, you may need to adjust downward. Therefore, aligning pricing with current market forces helps you stay competitive without losing margin.
Inventory planning also benefits. By knowing demand patterns, you can order the right amount at the right time. Additionally, this reduces excess stock while avoiding missed sales. You stop reacting and start planning based on real data.
Product development is another area where demand signals help. If customers consistently ask for certain features, you can build them with confidence. Therefore, conducting a supply and demand analysis can directly guide your product roadmap.
You should also use these insights when entering a new market. If supply is low but demand is growing, you may find an opportunity. However, entering a crowded space may require a different approach. Therefore, timing and positioning matter.
When you rely on supply and demand data, your decisions carry less risk. You stop guessing and start responding to actual market behavior. Additionally, this kind of analysis supports both short-term moves and long-term growth.
Conclusion
Making smart business decisions depends on how well you understand your market. Supply and demand shape nearly every outcome you face. Therefore, learning how they interact gives you a clear advantage. You move from reacting to planning with intent.
Additionally, each part of your operation connects to these forces. Pricing, inventory, and product choices all follow the signals that supply and demand provide. When you track trends and study the numbers, your choices become more accurate. You stop relying on opinions and start working with facts.
Conducting a supply and demand analysis helps you tie your strategy to actual market behavior. That means fewer surprises and better results. However, your work does not stop with one review. Markets shift, preferences change, and competitors adapt. Therefore, you need to revisit your analysis on a regular basis.
You can start small by tracking a few key metrics each month. Over time, this becomes part of your routine. Additionally, listening to your customers helps you confirm what the data shows. That balance helps you respond faster and stay aligned with demand. When you make decisions based on clear signals, you build more than efficiency. You build confidence in your direction. Therefore, supply and demand analysis is not only useful—it becomes a core part of how you grow.