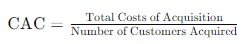Understanding and managing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is crucial for any organization looking to thrive. CAC measures the total cost of acquiring new customers, encompassing everything from marketing and sales expenses to administrative costs. It is a key metric that directly influences a company’s profitability and operational efficiency. By examining CAC in detail, businesses can optimize their strategies to attract customers more effectively while controlling costs. This analysis offers valuable insights into how CAC impacts a company’s financial health and its interactions with other critical business metrics. This includes Lifetime Value (LTV), retention rates, and Return on Investment (ROI). We’ll also address the nuances of CAC, providing a deeper understanding of its significance and how it can be leveraged for better business outcomes.
Definition and Importance of CAC
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a vital metric that quantifies the total expenses incurred to acquire a new customer. This encompasses marketing and advertising expenditures, sales team salaries, and other related costs. By measuring CAC, businesses gain crucial insights into the efficiency of their marketing strategies. It also shows the direct financial impact of acquiring new customers on their bottom line.
Understanding and managing CAC is essential for maintaining profitability. A lower CAC means that a company is able to attract customers without overspending, thereby maximizing profit margins. Conversely, a high CAC can quickly deplete resources, potentially leading to financial instability. Therefore, businesses strive to optimize their acquisition strategies to maintain a sustainable CAC. This ensures that the cost to acquire each new customer does not exceed the revenue they generate.
Moreover, CAC plays a significant role in assessing long-term sustainability. By regularly evaluating this metric, companies can adjust their marketing efforts to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Furthermore, a balanced CAC is indicative of a healthy customer turnover rate and effective market penetration strategies. A well-managed CAC not only boosts short-term financial outcomes. It also strengthens long-term business prospects by fostering a loyal customer base and enhancing market competitiveness.
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is essential for businesses to understand the efficiency of their marketing. It also helps to optimize their investment in customer acquisition. The formula for CAC is straightforward:
Customer Acquisition Cost equals the Total Costs of Acquisition divided by the Number of Customers Acquired.
The “Total Costs of Acquisition” includes all expenses directly related to acquiring new customers. These costs typically encompass marketing and advertising expenses. These funds are spent on campaigns and promotions aimed at attracting new customers. Additionally, sales team salaries are included, accounting for the compensation of sales personnel who directly contribute to customer acquisition. Overhead costs associated with acquisition efforts, such as technology and administrative expenses that support the sales and marketing teams, also factor into this total.
For example, suppose a company spends $100,000 on marketing and advertising, $50,000 on sales team salaries, and $20,000 on related overhead in a given period. If during that same period, the company acquires 1,000 new customers, the CAC would be calculated as follows:
Customer Acquisition Cost equals ($100,000 plus $50,000 plus $20,000) divided by 1,000
This calculation means that it costs the company $170 to acquire each new customer. By understanding this figure, businesses can evaluate the effectiveness of their marketing strategies. They can also make informed decisions about where to allocate resources for optimal customer acquisition. Additionally, monitoring changes in CAC over time helps businesses identify trends, assess the impact of new strategies, and ensure sustainable growth.
Factors Influencing CAC
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is influenced by a multitude of factors that vary across different industries and business models. The industry in which a company operates can significantly affect CAC due to differences in competition levels, customer demand, and typical marketing expenses. For example, highly competitive industries such as technology or fashion often require more aggressive and costly marketing strategies. This can increase CAC.
Additionally, a company’s business model plays a crucial role in shaping its CAC. Subscription-based services might see a higher initial CAC but benefit from longer customer lifecycles and recurring revenue. Whereas e-commerce businesses might experience lower CAC but with potentially shorter customer lifecycles. Similarly, market conditions such as economic downturns or surges in demand can lead to fluctuations in CAC. Businesses might need to increase incentives or discounts to attract customers during tough times, which raises acquisition costs.
Changes in strategy, such as adopting new marketing channels or targeting different customer segments, also impact CAC. For instance, if a company shifts from using traditional advertising to digital marketing, the CAC may initially rise due to the learning curve and setup costs. However, this strategy could potentially lower CAC over time through more targeted campaigns and data-driven decision-making.
Understanding these factors is essential for businesses to manage and optimize their CAC effectively. By monitoring how these elements affect customer acquisition, companies can adjust their strategies proactively to ensure sustainable growth and profitability in the face of evolving market dynamics.
Strategies to Reduce CAC
Reducing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is vital for enhancing a company’s profitability and efficiency. One effective strategy is improving conversion rates. By enhancing the user experience on websites and optimizing landing pages, businesses can convert a higher percentage of visitors into customers, thereby lowering CAC. For instance, implementing A/B testing to determine the most effective calls to action or page designs can lead to significant improvements in conversion rates.
Another approach to reducing CAC is optimizing marketing campaigns. This involves analyzing data to understand which channels deliver the highest ROI and adjusting spending accordingly. Businesses that shift their focus towards high-performing channels and fine-tune their messaging based on customer feedback often see a decrease in CAC. For example, a tech startup may find that social media campaigns yield more customers at a lower cost compared to pay-per-click advertising, leading to a strategic reallocation of their marketing budget.
Leveraging organic traffic is also a cost-effective way to reduce CAC. SEO and content marketing are long-term strategies that can significantly lower costs by attracting customers naturally through search engines without direct advertising expenses. A retail company, by focusing on keyword-rich content and user engagement, could enhance its search engine rankings and attract more organic visitors, thus reducing reliance on paid advertising.
Refining the sales process can further reduce CAC by making it more efficient and effective. Streamlining lead qualification and nurturing processes ensures that sales efforts are focused on the most promising leads, increasing the likelihood of conversion. A B2B service provider, for example, might implement a CRM system to better track interactions and tailor follow-ups based on specific customer data and previous engagements.
By adopting these strategies, businesses can successfully lower their CAC, improve profitability, and ultimately sustain competitive advantage in their markets.
CAC in Relation to Other Key Metrics
Understanding the relationship between Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and other critical business metrics, such as Lifetime Value (LTV), retention rates, and Return on Investment (ROI), is essential for ensuring sustainable business growth and profitability. LTV, which measures the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer over the course of their relationship, is particularly important when compared to CAC. A healthy ratio of LTV to CAC (typically 3:1 or higher) indicates that a company is generating significant value from its customers relative to the cost of acquiring them.
Furthermore, retention rates are closely tied to both CAC and LTV. High retention rates often lead to a higher LTV, as ongoing relationships typically mean continued revenue from existing customers. This dynamic can also contribute to a lower CAC over time, as the cost of maintaining relationships is generally lower than the cost of acquiring new customers. Businesses that focus on improving customer satisfaction and engagement usually see an increase in retention rates, which positively affects both profitability and LTV.
ROI is another critical metric that interacts with CAC. ROI measures the efficiency and profitability of investment into customer acquisition efforts. A positive ROI means that the returns from these investments exceed the costs, which includes CAC. Balancing CAC with ROI involves optimizing marketing and sales strategies. This ensures that each dollar spent on acquisition generates the maximum possible return.
To maintain healthy business growth, companies must carefully balance CAC with these metrics. It involves continuous monitoring and adjustments based on performance data. By doing so, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance customer value, optimize investment returns, and sustain long-term profitability. This strategic alignment helps companies not only to survive but to thrive in competitive markets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and strategically managing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is pivotal for any business aiming to enhance profitability and sustain growth. By examining how CAC interacts with other vital metrics such as Lifetime Value (LTV), retention rates, and Return on Investment (ROI), businesses can gain comprehensive insights into their financial health and operational efficiency. It’s essential to maintain a favorable balance between these metrics. Doing so ensures that investment in customer acquisition is both prudent and productive. Adopting targeted strategies to optimize CAC boosts short-term financial outcomes. It also strengthens the foundation for long-term business success, fostering a cycle of growth and profitability that benefits all stakeholders.