The Nature of Cybersecurity Threats
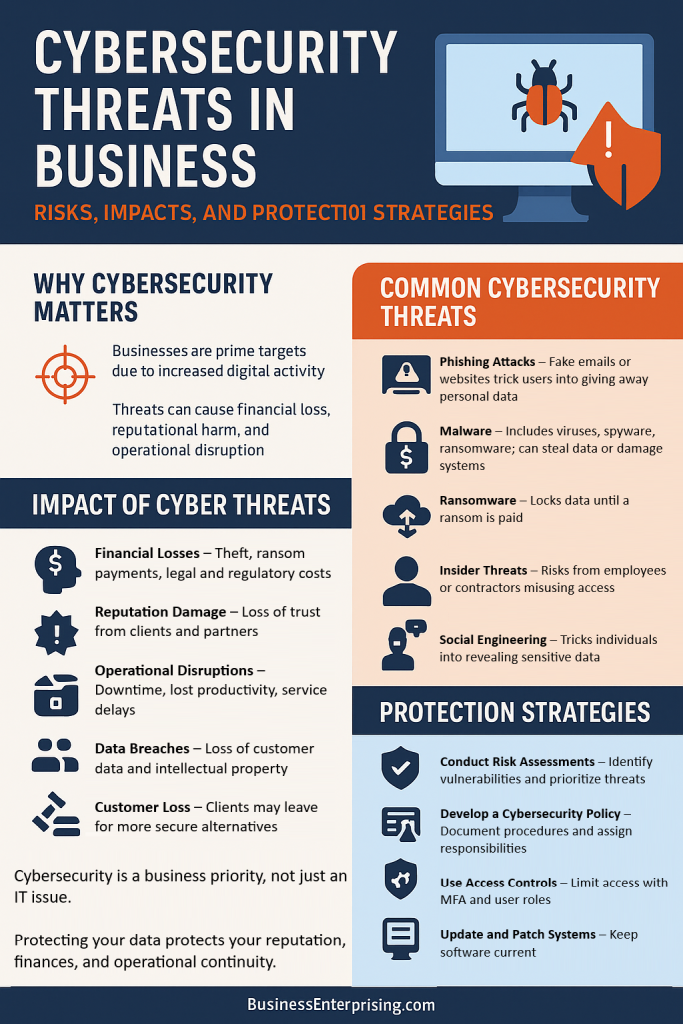
Cybersecurity threats in business come in various forms, each posing unique risks:
Phishing Attacks: Phishing involves deceptive attempts to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. Phishing attacks are typically carried out through email, social media, or malicious websites.
Malware: Malware, or malicious software, includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, as well as spyware. These malicious programs can infiltrate computer systems, steal data, damage files, and disrupt operations.
Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. This type of attack can cripple business operations and result in significant financial losses.
DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm a network or website with traffic, causing it to slow down or crash. DDoS attacks can also disrupt business operations and online services.
Insider Threats: In addition, insider threats involve malicious or negligent actions by employees, contractors, or other insiders who have access to a company’s systems and data. These threats can be particularly challenging to detect and prevent.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are prolonged and targeted cyberattacks in which an intruder gains access to a network and remains undetected for an extended period. APTs are typically carried out by highly skilled attackers, often with specific objectives such as data theft or espionage.
Social Engineering: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. This can include tactics such as pretexting, baiting, and tailgating.
Potential Impacts of Cybersecurity Threats
The consequences of cybersecurity threats can be severe and far-reaching:
Financial Losses: Cyberattacks can lead to direct financial losses due to theft, fraud, and ransom payments. Additionally, businesses may incur costs related to incident response, legal fees, and regulatory fines.
Reputational Damage: A cyberattack can severely damage a company’s reputation. Customers, partners, and stakeholders may lose trust in the business, leading to decreased sales and lost opportunities.
Operational Disruptions: Cyberattacks can disrupt business operations, causing downtime, loss of productivity, and delays in service delivery. This can have a cascading effect on the entire supply chain.
Data Breaches: Data breaches can result in the exposure of sensitive information, including customer data, intellectual property, and proprietary business information. This can lead to legal liabilities and compliance issues.
Customer Loss: Customers are increasingly concerned about data privacy and security. A breach can lead to customer churn as individuals seek more secure alternatives.
Regulatory Consequences: Businesses may face regulatory consequences and penalties if they fail to comply with data protection and cybersecurity regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Strategies for Safeguarding Against Cybersecurity Threats
To protect against cybersecurity threats, businesses should implement a comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity strategy:
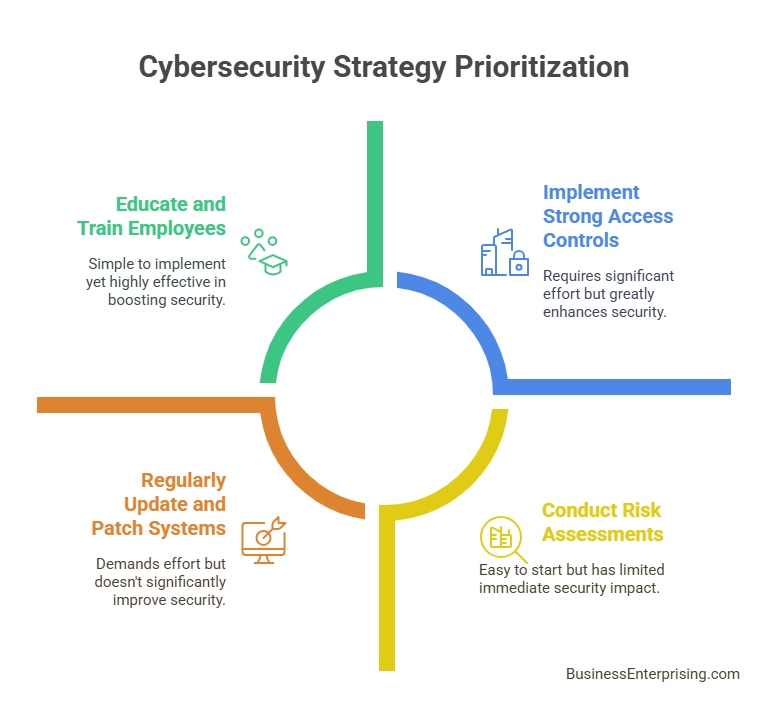
Conduct Risk Assessments: Regularly assess and identify potential cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities. Understanding the specific threats your business faces allows you to prioritize and address them effectively.
Develop a Cybersecurity Policy: Establish a clear cybersecurity policy that outlines procedures, protocols, and responsibilities for safeguarding data and systems. Ensure that all employees are aware of and adhere to these policies.
Implement Strong Access Controls: Limit access to sensitive information and systems to authorized personnel only. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls to enhance security.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keep all software, systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly updating systems helps protect against known vulnerabilities.
Educate and Train Employees: Provide ongoing cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees. Educate them about common threats such as phishing and social engineering and teach them best practices for maintaining security.
More Cyberattack Protection Tips
Invest in Advanced Security Solutions: Implement advanced security solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and encryption. These tools can help detect and prevent cyber threats.
Monitor and Respond to Threats: Establish a security operations center (SOC) or use managed security services to monitor for suspicious activity and respond to incidents in real-time. Early detection and response can minimize the impact of cyberattacks.
Create an Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a cyberattack. This plan should include procedures for containment, eradication, recovery, and communication.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Perform regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of your security measures. This proactive approach helps identify weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations: Stay informed about relevant cybersecurity and data protection regulations. Ensure that your business complies with these regulations to avoid legal consequences and enhance overall security.
Cybersecurity threats in business pose significant risks, but with a proactive and comprehensive approach, these risks can be managed and mitigated. By conducting risk assessments, implementing strong access controls, educating employees, investing in advanced security solutions, and regularly monitoring and responding to threats, businesses can enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect against potential attacks.
In an increasingly digital world, cybersecurity is not just an IT issue but a business imperative. Ensuring the security of your data and systems is crucial for maintaining customer trust, protecting financial assets, and ensuring the continuity of your operations. By prioritizing cybersecurity, businesses can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape with confidence and resilience.