Traditional business planning often relies on predicting the future, but Effectuation Theory takes a different path. It emphasizes decision-making based on what’s currently possible, enabling you to adjust as new opportunities arise. This method doesn’t require a detailed roadmap, allowing you to adapt quickly without taking on excessive risk. For many startups, Effectuation Theory provides a practical framework that embraces resourcefulness and real-world learning, making it a valuable strategy in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Understanding Effectuation Theory: Origins and Core Principles
Effectuation Theory offers a practical framework for entrepreneurs, focusing on using existing resources to create new ventures. Developed by Saras Sarasvathy, this approach shifts from traditional business planning to an adaptive, resource-based strategy. Rather than following a fixed path, entrepreneurs using effectuation adjust their direction based on available means and emerging opportunities. This perspective encourages flexibility and responsiveness, which are essential in uncertain markets.
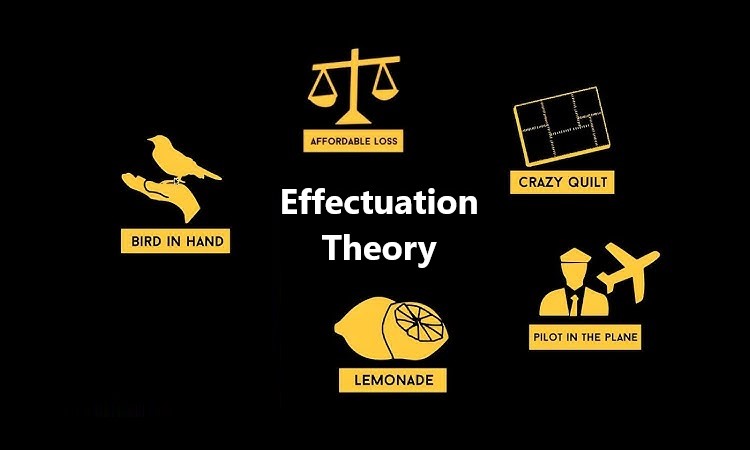
Effectuation Theory is grounded in five key principles. The Bird-in-Hand principle encourages you to start with what you have—your skills, connections, and resources—and build from there. The Affordable Loss principle suggests investing only what you can afford to lose. This approach reduces risk, making it easier to pivot as new information arises. The Lemonade principle involves embracing surprises, treating unexpected events as chances to innovate, rather than setbacks.
The Crazy Quilt principle emphasizes forming partnerships. By collaborating with others, you can share resources and expand opportunities. Finally, the Pilot-in-the-Plane principle highlights the importance of control over prediction. Instead of trying to predict the future, you shape it through your decisions and actions. Together, these principles provide a dynamic toolkit for entrepreneurs. They allow you to adapt, minimize risk, and make the most of every opportunity.
Effectuation vs. Causation: A Different Approach to Entrepreneurship
Traditional entrepreneurship often relies on a causation-based approach, where you set specific goals and work backward to achieve them. This method requires detailed planning, predicting market demands, and creating a fixed roadmap for success. Causation assumes a stable environment, allowing for clear steps from start to finish. However, in dynamic and uncertain markets, this approach can limit adaptability, especially when unexpected challenges or opportunities arise.
Effectuation Theory offers a different perspective. Instead of starting with a fixed goal, effectuation encourages you to use available resources and adjust as conditions change. This flexible approach allows you to embrace uncertainty rather than fearing it. In effectuation, your focus shifts from rigid plans to exploring potential outcomes based on what you know and have at hand. As a result, you can pivot easily, adapting strategies when new information or partnerships emerge.
With Effectuation Theory, your decision-making process becomes more agile and opportunity-driven. Rather than sticking to a predetermined path, you create multiple options as your resources, connections, and insights evolve. This method reduces dependence on forecasting and allows for continuous learning. In a rapidly changing business environment, effectuation’s adaptability provides a practical advantage over traditional causation, helping you respond effectively to unpredictable situations.
Applying Effectuation in Startups: Leveraging Existing Resources
Effectuation Theory’s Bird-in-Hand principle encourages startups to start with available resources, focusing on what they already have rather than waiting for ideal conditions. By leveraging your team’s skills, networks, and expertise, you can create value without a fixed roadmap or heavy reliance on external funding. This approach allows you to begin testing ideas right away, helping you adapt and refine your business concept with real feedback from early experiences.
Utilizing networks, for instance, can be an effective way to gather insights and even attract initial customers. Friends, colleagues, and industry connections can offer advice, collaborations, and referrals, reducing the need for costly marketing efforts. Your team’s skills are another powerful resource. When you focus on what your team does best, you can make steady progress without outsourcing or hiring outside expertise.
This resource-driven approach of Effectuation Theory keeps you nimble. You don’t need to commit to long-term goals or complex strategies at the start. Instead, you can adjust plans as new opportunities or challenges arise. By starting with what’s available and continuously learning, you can build a business model that’s grounded in real-world conditions. This flexibility is invaluable in fast-changing markets, where rigid plans often fall short. With Effectuation Theory, your startup grows through practical, achievable steps based on the resources and knowledge you already have.
Navigating Uncertainty and Risk with the Affordable Loss Principle
Effectuation Theory’s Affordable Loss principle helps entrepreneurs make decisions based on what they can afford to lose, not just potential gains. This mindset encourages you to focus on manageable risks rather than taking large financial leaps. By setting limits on investment, you protect your resources and minimize potential setbacks, which is especially important in unpredictable markets.
For startups in volatile industries, the Affordable Loss principle provides a safer way to test ideas. You can experiment with minimal resources, assessing the results without risking too much capital. This approach allows you to make small, incremental moves rather than committing to large-scale investments that may or may not pay off. It’s a strategic way to move forward without stretching your resources too thin.
This principle shifts your attention from big returns to sustainable progress. Instead of pursuing high-stakes opportunities, you focus on realistic, attainable actions. Each step becomes a low-risk way to learn and adapt, preparing you for potential shifts in the market. By concentrating on affordable losses, you create a buffer against failure, allowing your business to pivot easily as conditions change. In the end, Effectuation Theory’s Affordable Loss principle helps you build resilience and adaptability in uncertain environments.
Building Partnerships and Expanding Networks: The Crazy Quilt Principle
Effectuation Theory’s Crazy Quilt principle emphasizes the value of building partnerships and expanding networks. Rather than seeing others as competitors, you focus on collaboration and co-creation. Working with partners brings diverse perspectives and resources, which can open unexpected opportunities for your business. When you form alliances, you share the journey, reducing the risks and challenges that often arise in entrepreneurship.
Collaboration allows you to leverage others’ strengths while contributing your own, creating a mutually beneficial relationship. These partnerships aren’t just about resources; they’re about combining expertise and insights to create something greater than either could alone. This approach shifts your mindset from competition to cooperation, helping you find new paths forward that may have been inaccessible on your own.
The Crazy Quilt principle also provides flexibility. As you work with partners, you adapt and respond to changes together. Each partner’s unique contribution shapes the outcome, allowing you to pivot based on collective knowledge and support. Building this collaborative network doesn’t only reduce your risk; it creates a dynamic environment where shared goals and resources drive growth. In unpredictable markets, the Crazy Quilt principle within Effectuation Theory gives you a stable base of support and shared innovation, strengthening your ability to grow and adapt.
Real-World Examples of Effectuation in Action
Effectuation Theory has influenced many businesses to build success from limited resources, adaptive strategies, and collaborative approaches. One prominent example is Airbnb, which started with founders leveraging their apartment and existing contacts. Instead of waiting for significant investment, they focused on available resources to test their concept. By initially renting out air mattresses in their living room, they adapted their service model based on feedback, using partnerships and community engagement to grow their network. This approach allowed them to learn, adjust, and expand without heavy upfront investment.
Another example is Dropbox, which applied the Affordable Loss principle to gain initial users without extensive marketing. Instead of risking large sums on advertising, Dropbox shared a video demo of their product, generating interest and collecting feedback before launching fully. This allowed them to minimize financial risk while gathering essential market insights. By focusing on what they could afford to lose, Dropbox grew steadily, adapting to user demands without overcommitting resources.
Zappos also embodies Effectuation Theory, using partnerships and adaptability to build its brand. In its early days, Zappos partnered with local stores, using their existing inventory rather than investing in stock. This Crazy Quilt approach allowed Zappos to expand its offerings with minimal risk. By collaborating rather than competing, they grew their network and created a trusted brand. These examples highlight how businesses can thrive by adapting strategies to their resources, networks, and evolving market conditions.
Conclusion
Effectuation Theory provides a practical approach for entrepreneurs who face uncertainty and limited resources. By focusing on what you already have and building partnerships, you can adapt to changing conditions without excessive risk. This method allows you to move forward even without a fixed roadmap, helping you stay flexible and responsive to new opportunities. Effectuation’s principles encourage sustainable growth, reducing dependence on forecasts and traditional planning.
For startups and small businesses, Effectuation Theory offers a realistic, resource-driven path to success. Rather than betting everything on a single plan, you learn to make smaller, manageable decisions. This approach also creates room for collaboration, which can strengthen your business and expand your network. Embracing effectuation means valuing adaptability, resourcefulness, and real-time learning as you grow your venture.