By adopting lean practices, you create a more agile and customer-focused organization. However, implementing these methods requires careful planning and ongoing commitment. Continuous improvement and measurable results are key to sustaining progress and delivering consistent value.
Lean business operations are not limited to any specific industry or company size. Whether you run a small business or a large organization, lean principles offer practical tools to enhance performance. Understanding how to apply these strategies can lead to long-term growth and competitive advantage.
What is Lean Business Operations?
Lean business operations focus on minimizing waste while maximizing value for your customers. This approach emphasizes efficiency in processes and resource use. By streamlining operations, businesses can deliver high-quality products and services while reducing costs.
At its core, lean operations aim to eliminate activities that do not add value. These include unnecessary steps, excess inventory, and time-consuming delays. Additionally, lean practices prioritize understanding customer needs and tailoring processes to meet those expectations effectively.
The concept originated in manufacturing but applies to various industries today. For example, lean methods are used in healthcare, technology, and service sectors to improve performance. By adopting lean business operations, you can create a more agile and customer-focused organization.
Continuous improvement is a key principle of lean operations. This involves regularly assessing workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and making incremental changes. Therefore, lean practices help your business stay competitive and adapt to changing demands.
By focusing on lean business operations, you can build a more efficient, customer-centered, and sustainable business. This approach not only improves profitability but also enhances your ability to deliver value consistently.
Key Principles of Lean Operations
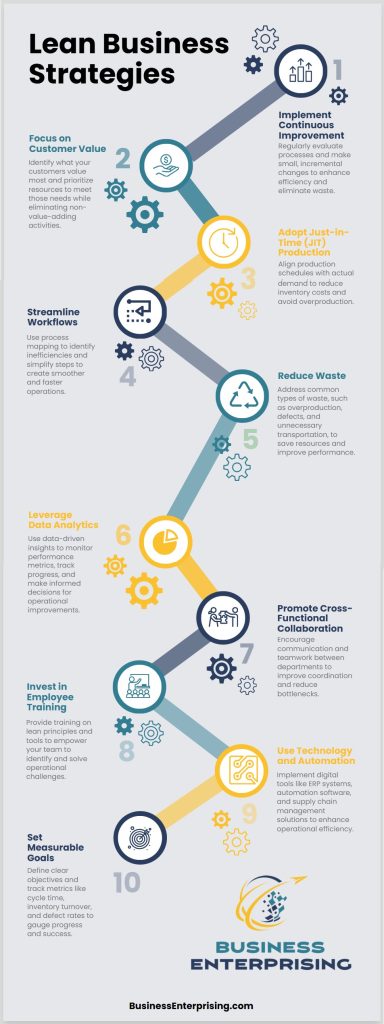
Lean business operations rely on key principles that improve efficiency and deliver value to your customers. These principles guide organizations in eliminating waste, focusing on customer needs, and optimizing workflows. By implementing them, you can create processes that are more effective and adaptable.
Continuous improvement is a foundational principle of lean operations. It encourages businesses to regularly evaluate and refine their workflows. This approach involves identifying inefficiencies, testing new solutions, and making incremental changes. Therefore, it fosters a culture of learning and adaptability.
Customer focus is another essential element. Lean operations prioritize understanding what your customers value most. By tailoring your processes to meet these expectations, you can increase satisfaction while reducing unnecessary steps. Additionally, this principle helps you build stronger customer relationships over time.
Waste elimination is central to lean practices. This includes reducing excess inventory, minimizing downtime, and streamlining communication. By eliminating activities that do not add value, you can save resources and improve productivity. Additionally, this principle enhances your ability to respond quickly to changes in demand.
Just-in-time production aligns your resources with customer needs. This principle emphasizes producing goods or services only when required. As a result, you can avoid overproduction, lower storage costs, and improve cash flow. It also promotes better coordination between teams and suppliers.
By applying these principles, you can make lean business operations a core part of your strategy. This not only improves efficiency but also ensures your organization remains competitive in a fast-changing market.
Implementing Lean Processes in Small and Large Businesses
Implementing lean business operations can benefit both small and large businesses by improving efficiency and delivering greater value to customers. Although the scale of application differs, the core principles remain the same. By focusing on waste reduction, customer value, and continuous improvement, companies of any size can create more effective workflows.
Small businesses can start with simple tools and strategies. For example, using process mapping helps identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. Additionally, adopting digital tools like project management software can streamline communication and task tracking. Small-scale operations benefit from lean practices because they create flexibility and reduce unnecessary costs.
Larger companies often require a more structured approach. Implementing lean processes across departments involves cross-functional collaboration and standardized practices. For instance, using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can integrate data and optimize supply chains. Additionally, incorporating lean principles into team training ensures alignment across the organization and builds a culture of efficiency.
Scalability is a key advantage of lean methodologies. Strategies such as just-in-time production and regular process reviews adapt easily to businesses of varying sizes. Whether you’re managing a small team or a global enterprise, lean business operations promote agility and responsiveness.
By adopting lean processes, companies of all sizes can enhance productivity, reduce waste, and respond better to customer needs. These scalable strategies allow you to build a more efficient and competitive organization.
The Role of Technology in Lean Operations
Technology plays a significant role in supporting lean business operations by streamlining processes and improving decision-making. Digital tools like process automation, data analytics, and supply chain management software help organizations eliminate waste and increase efficiency. By integrating these tools, you can align operations with lean principles more effectively.
Process automation reduces repetitive tasks, saving time and resources. Automated workflows, for example, help you manage inventory levels and track production schedules in real-time. Additionally, automation minimizes errors, allowing your team to focus on more strategic activities that add value to your customers.
Data analytics enhances decision-making by providing insights into your operations. Analyzing key metrics such as cycle time and resource utilization helps identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Furthermore, predictive analytics allows you to anticipate demand changes, reducing waste and overproduction.
Supply chain management software ensures better coordination between suppliers and operations. These tools help track shipments, monitor inventory, and optimize delivery schedules. As a result, you can improve responsiveness and reduce unnecessary delays. Additionally, integrating supply chain systems with real-time data enhances collaboration across teams.
By leveraging technology, you can strengthen your lean business operations and adapt to changing demands. These tools not only improve efficiency but also help you deliver greater value to your customers. Embracing technology as part of your lean strategy ensures your business remains competitive in a fast-paced market.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Transitioning to lean business operations can present several challenges, but addressing them effectively ensures long-term success. One common obstacle is resistance to change within your team. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new methods or abandon familiar processes. Therefore, clear communication about the benefits of lean practices is essential. Providing training and involving your team in decision-making can also help ease the transition.
Another challenge is identifying inefficiencies in existing workflows. Without a structured approach, it can be difficult to pinpoint waste or unnecessary steps. Implementing tools like process mapping or conducting regular audits can uncover areas for improvement. Additionally, setting measurable goals allows you to track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Resource allocation can also be a concern, especially for smaller businesses. Lean operations often require an initial investment in tools, training, or technology. However, starting with small-scale pilot projects can minimize risks and demonstrate the value of lean practices. By gradually expanding these efforts, you can optimize your operations without overwhelming your resources.
Sustaining momentum is another challenge businesses face. Lean operations thrive on continuous improvement, which requires ongoing effort and commitment. Regularly reviewing processes, gathering employee feedback, and celebrating achievements can help maintain focus. Additionally, fostering a culture that values efficiency and customer satisfaction ensures lean practices remain embedded in your organization.
By addressing these challenges strategically, you can transition to lean business operations more effectively. These actionable solutions not only help overcome obstacles but also set the stage for long-term growth and success.
Measuring Success in Lean Operations
Measuring success in lean business operations requires tracking key performance metrics that reflect efficiency and value creation. Metrics like cycle time, inventory turnover, and defect rates provide insights into how well your processes align with lean principles. By monitoring these indicators, you can identify areas for improvement and celebrate progress.
Cycle time measures how long it takes to complete a process from start to finish. Shorter cycle times often indicate improved efficiency. Regularly reviewing this metric helps you identify bottlenecks and streamline workflows. Additionally, reducing cycle time enhances customer satisfaction by enabling faster delivery of products or services.
Inventory turnover tracks how quickly your inventory is sold or used within a given period. A higher turnover rate typically signals effective inventory management and reduced waste. Therefore, monitoring this metric helps you optimize ordering and avoid excess stock. By aligning inventory turnover with customer demand, you can reduce storage costs and improve cash flow.
Defect rates measure the frequency of errors or flaws in your products or services. This metric directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational costs. Lowering defect rates reflects higher quality and fewer resources spent on corrections. Additionally, addressing the root causes of defects supports continuous improvement.
Using these metrics allows you to assess the effectiveness of your lean business operations. Regularly analyzing and responding to these indicators ensures that your organization stays focused on delivering value. By prioritizing measurable outcomes, you can maintain a culture of efficiency and sustained success.
Conclusion
Lean business operations offer a practical way to improve efficiency and create more value for your customers. By focusing on reducing waste, optimizing processes, and using measurable metrics, you can ensure continuous improvement. Additionally, adopting lean practices helps your business remain competitive in a fast-changing market.
However, transitioning to lean operations requires commitment and thoughtful planning. Addressing challenges, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of efficiency are essential steps. Regularly tracking performance ensures your efforts align with both your goals and customer expectations.
By implementing lean business operations, you can build a more agile and productive organization. This approach not only enhances performance but also supports sustainable growth over time.