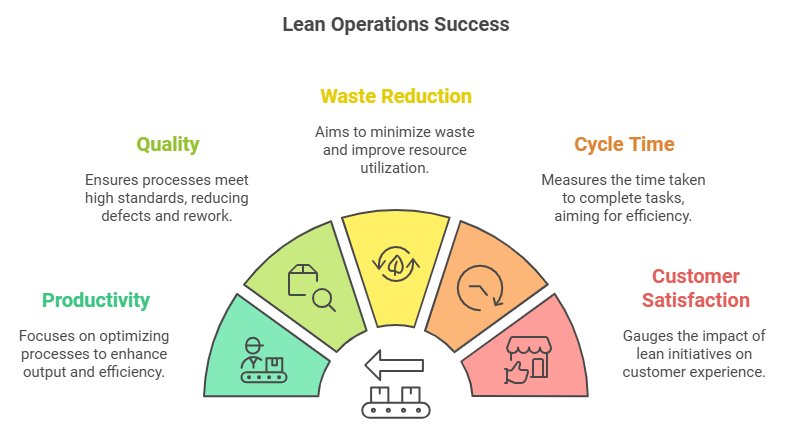
Lean operations focus on eliminating unnecessary steps and reducing resource use. From cutting down cycle times to optimizing inventory, each lean technique helps make your business more efficient. With lean practices in place, your team can prioritize quality, improve customer satisfaction, and lower operational costs. Embracing lean operations can set a strong foundation for sustainable growth and ongoing success.
Understanding the Principles of Lean Operations
Understanding the principles of lean operations is fundamental to building efficient processes that drive business success. Lean methodology focuses on reducing waste, optimizing resources, and delivering high value to customers. By minimizing unnecessary steps and materials, you streamline operations and make your business more adaptable to changes in demand.
One core aspect of lean operations for success is continuous improvement. This principle emphasizes ongoing assessment and refinement of processes to maintain efficiency and quality. By encouraging teams to identify areas for improvement regularly, you create a culture that supports productivity and growth. Continuous improvement also allows you to respond quickly to market needs, giving your business a competitive edge.
Another principle of lean methodology is maximizing customer value. Lean operations aim to align processes closely with customer expectations, focusing on delivering high-quality products or services. When customer needs guide your operational decisions, you build stronger relationships and improve customer satisfaction. Together, these lean principles set a solid foundation for sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Identifying and Eliminating Waste
Identifying and eliminating waste is essential for lean operations for success. Waste comes in many forms, with common types including overproduction, waiting time, and excess inventory. Overproduction occurs when you produce more than demand requires, leading to unused products and wasted resources. By aligning production closely with demand, you can reduce overproduction and allocate resources more effectively.
Waiting time is another form of waste that impacts efficiency. This waste happens when materials, information, or employees are idle due to delays or bottlenecks in the process. Reducing waiting time requires analyzing workflows and identifying areas where delays commonly occur. Streamlining these areas with clear communication and efficient scheduling helps maintain steady productivity.
Excess inventory, or holding more stock than needed, also contributes to waste by increasing storage costs and the risk of product obsolescence. To combat this, you can implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, which focus on stocking materials only as they’re needed. By actively managing these types of waste, you can make your operations leaner, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
Measuring Success in Lean Operations
Measuring success in lean operations requires selecting the right key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the impact of your lean initiatives. By tracking these metrics, you gain insights into whether your processes align with lean goals. For lean operations for success, KPIs should focus on areas like productivity, quality, and waste reduction.
Cycle time is a key metric, indicating the time required to complete a specific task or process. Reducing cycle time can reveal improvements in efficiency, showing how well your lean strategies are working. Similarly, tracking defect rates helps assess the quality of your processes. Lowering defect rates not only enhances product quality but also minimizes the costs associated with rework or waste.
Another essential KPI is inventory turnover, which measures how efficiently you’re managing inventory. A higher turnover rate typically means your process is leaner, with less capital tied up in unused stock. Customer satisfaction scores can also serve as an indirect measure of lean success, as faster, more efficient processes often result in better service. By monitoring these KPIs regularly, you create a structured approach to evaluating and improving lean operations, ensuring ongoing progress and alignment with business objectives.
Implementing Process Improvement Techniques
Implementing process improvement techniques is a key component of lean operations for success. Techniques like Kaizen, Six Sigma, and 5S are widely used to improve efficiency and streamline workflows. Kaizen, which means “continuous improvement” in Japanese, encourages small, incremental changes across all levels of an organization. By empowering employees to suggest and implement improvements regularly, Kaizen creates a culture focused on ongoing development and refinement.
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and improving quality by identifying and controlling variation in processes. This technique uses data analysis to pinpoint problem areas, ensuring that improvements are based on measurable insights. Six Sigma not only enhances product quality but also helps reduce costs associated with errors or waste. Businesses that adopt Six Sigma often see increased efficiency, higher customer satisfaction, and improved profitability.
The 5S method is another effective tool for streamlining operations, particularly in physical workspaces. The five steps—Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—help create organized and efficient environments. By following these steps, you can reduce clutter, improve safety, and make workflows more manageable. When used together, Kaizen, Six Sigma, and 5S provide a comprehensive approach to optimizing processes, making your business more agile and responsive to change.
Enhancing Employee Engagement in Lean Operations
Employee engagement is essential for lean operations for success, as it encourages a culture of continuous improvement. When employees actively participate in identifying and solving issues, they feel a sense of ownership and responsibility. This involvement motivates them to suggest innovative ideas, refine processes, and help reduce waste. Engaging employees in lean operations not only boosts morale but also improves productivity and efficiency.
Training is a key factor in fostering a lean culture. By offering ongoing education on lean principles and techniques, you empower employees with the tools to contribute effectively. Training sessions on methodologies like Kaizen and 5S help employees understand their roles in the larger lean strategy. With the right knowledge, your team can make informed decisions that align with your company’s lean objectives.
Regular feedback and open communication are also critical in supporting engagement. Encouraging employees to share their insights and acknowledging their contributions builds trust and reinforces commitment to lean practices. When employees see the impact of their efforts, they become more invested in maintaining and improving lean operations. By emphasizing engagement, training, and communication, you create a strong foundation for lean operations that drives both personal and organizational growth.
Leveraging Technology for Lean Operations
Leveraging technology is essential for lean operations for success, as it enhances efficiency and precision in daily workflows. Automation, for instance, eliminates repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities. By automating processes like data entry or quality control, you reduce the risk of human error and speed up operations. This not only saves time but also minimizes costs associated with waste.
Real-time data tracking is another powerful tool that supports lean principles. With real-time insights, you can monitor performance instantly, identifying issues as they arise. This immediate access to data allows your team to make quick adjustments, maintaining high productivity and avoiding costly delays. Real-time tracking also helps you gather insights on process efficiency, which can drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Process management software further optimizes workflows by centralizing tasks, schedules, and resources in one platform. With a unified view, your team can coordinate seamlessly, reducing communication gaps and improving project timelines. Additionally, these tools provide valuable data analytics that highlight areas for improvement. By integrating automation, data tracking, and process management, you create a streamlined, responsive operation that aligns with lean goals, positioning your business for sustained success.
Conclusion
Achieving lean operations for success involves a commitment to continuous improvement, waste reduction, and effective use of resources. By implementing lean principles, you create more efficient workflows, increase productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction. From employee engagement to technology integration, each element plays a critical role in building a sustainable lean culture.
Regularly measuring KPIs ensures that your lean initiatives stay on track and deliver measurable results. Tracking metrics like cycle time, defect rates, and inventory turnover provides valuable insights, guiding further improvements. As you refine these processes, your business becomes more agile and better equipped to respond to changing demands. Lean operations not only reduce costs but also foster a culture focused on quality and efficiency. By embracing these practices, you lay a strong foundation for long-term growth and resilience.