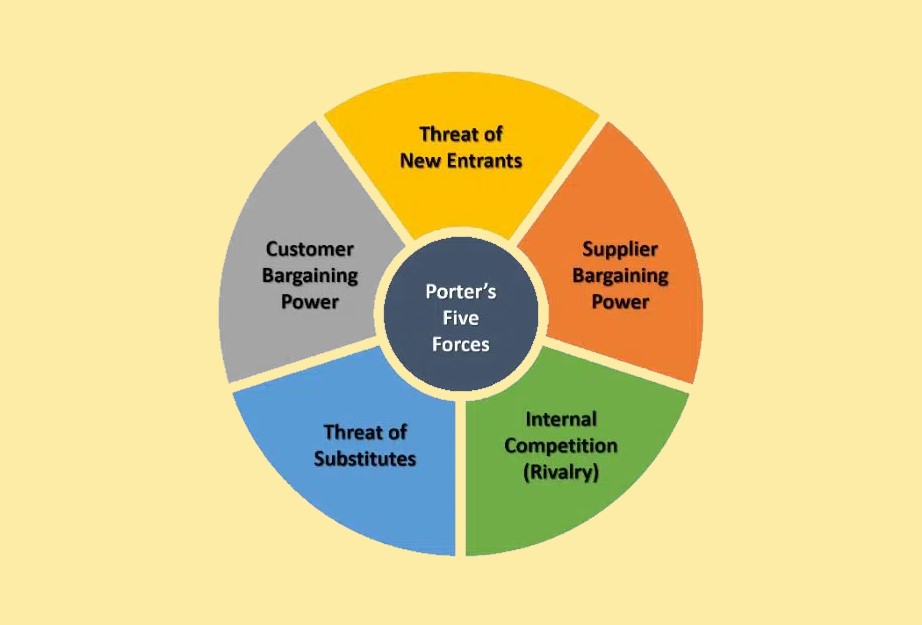
Porter’s Five Forces Model is one of the most influential frameworks for understanding the competitive forces shaping industries. Developed by Michael E Porter in 1979, this model helps businesses analyze the intensity of competition in their market and the potential profitability within an industry. By understanding these forces, companies can create strategies to enhance their competitive position and improve their long-term profitability. As business environments become increasingly complex, Porter’s Five Forces Model remains essential for companies seeking to navigate their competitive landscapes successfully.
Porter’s Five Forces Model is one of the most influential frameworks for understanding the competitive forces shaping industries. Developed by Michael E Porter in 1979, this model helps businesses analyze the intensity of competition in their market and the potential profitability within an industry. By understanding these forces, companies can create strategies to enhance their competitive position and improve their long-term profitability. As business environments become increasingly complex, Porter’s Five Forces Model remains essential for companies seeking to navigate their competitive landscapes successfully.
At the core of Porter’s Five Forces Model are five key forces that shape the structure and competitive intensity of an industry. These forces include the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. Understanding how these forces influence an industry helps companies develop strategies to address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
The Power of Buyers in Porter’s Five Forces Model
One of the central forces in Porter’s Five Forces Model is the bargaining power of buyers. This force examines how much power customers have in influencing pricing, product offerings, and terms of sale within an industry. When buyers have significant leverage, they can push for lower prices, better quality, or improved service. This can reduce profitability for companies. Factors such as the availability of alternative products, price sensitivity, and the concentration of buyers in the market can influence their power.
For example, in industries where products are highly standardized and easily substitutable, buyers tend to have more bargaining power. In contrast, when companies offer highly differentiated products, buyer power diminishes, as customers have fewer alternatives. To mitigate the power of buyers, businesses can focus on improving product differentiation, enhancing customer loyalty, or finding ways to increase switching costs. These strategies make it more difficult for buyers to seek alternatives, thereby reducing their leverage.
Supplier Power and Its Impact on Industry Dynamics
Another crucial element in Porter’s Five Forces Model is the bargaining power of suppliers. Suppliers can exert influence on an industry by raising prices, limiting quality, or reducing the availability of essential inputs. When suppliers hold considerable power, they can erode industry profitability by increasing costs for companies within the market. Supplier power is generally higher when there are fewer suppliers, when switching suppliers is costly, or when suppliers offer products that are essential to the company’s operations.
To reduce supplier power, companies can explore strategies such as diversifying their supplier base, developing stronger relationships with key suppliers, or vertically integrating to gain more control over the supply chain. By reducing their dependence on powerful suppliers, businesses can protect their margins and improve their competitive position within the industry.
The Threat of New Entrants and Industry Barriers
The threat of new entrants is another key force in Porter’s Five Forces Model. This force assesses how easy or difficult it is for new competitors to enter the market. If entry barriers are low, new competitors can quickly enter the industry, increasing competition and reducing profitability for existing firms. Factors such as economies of scale, access to distribution channels, brand loyalty, and regulatory requirements can act as barriers to entry.
To protect against the threat of new entrants, companies should invest in building strong brands or achieving cost leadership. The can also create proprietary technology that is difficult for competitors to replicate. These strategies can raise the barriers to entry and make it more challenging for new competitors to establish themselves in the market.
Substitutes and Their Influence on Market Stability
The threat of substitute products or services is another important aspect of Porter’s Five Forces Model. This force evaluates how easily customers can switch to alternative products or services that fulfill the same need. The more substitutes available, the higher the threat to a company’s market position. This is because customers can choose alternatives that may offer lower prices or better features. For example, the rise of streaming services has been a significant substitute threat to traditional cable television providers.
Companies facing the threat of substitutes must differentiate their products and services to offer unique value that cannot be replicated. Additionally, businesses should focus on innovation, improving customer service, and building stronger relationships with their customers to minimize the impact of substitutes on their market position.
Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
The final force in Porter’s Five Forces Model is the intensity of competitive rivalry. This force examines the level of competition among existing players in the industry. When rivalry is intense, companies often engage in price wars, aggressive marketing campaigns, and constant innovation. These can reduce profitability for all players. Factors such as the number of competitors, market growth rate, and product differentiation can influence the intensity of rivalry.
To succeed in highly competitive markets, companies must focus on developing clear differentiation strategies. Optimizing operational efficiency and seeking ways to offer superior value to customers are also helpful. Firms that can find ways to outcompete their rivals through innovation, customer service, or cost advantages are better positioned to thrive in competitive environments.
The Relevance of Porter’s Five Forces Model Today
Although Porter’s Five Forces Model was developed decades ago, it remains highly relevant in today’s complex and dynamic business world. The model offers businesses a clear framework for analyzing industry dynamics and identifying areas for improving competitive positioning. In an era of globalization, technological advancement, and shifting consumer behaviors, Porter’s Five Forces Model provides valuable insights for companies navigating uncertainty and competition.
By regularly applying the model, companies can anticipate market changes, respond to competitive pressures, and make informed strategic decisions. Whether in traditional or emerging industries, Porter’s Five Forces Model helps businesses understand external forces shaping profitability and competition.
In conclusion, Porter’s Five Forces Model is crucial for businesses aiming to analyze industry competition and improve their market position. By examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and competitive rivalry, companies gain a deeper understanding of profitability drivers. Companies using the model are better equipped to develop strategies that protect market position and ensure long-term success.