Porter’s Generic Strategies are a foundational framework for businesses aiming to achieve a competitive edge in their industry. Developed by Michael Porter, this model outlines three key approaches: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Each strategy offers a distinct path for businesses to position themselves effectively against competitors. Companies that successfully adopt these strategies can improve market performance and create lasting value for their customers. Understanding how to apply Porter’s Generic Strategies is crucial for businesses looking to navigate today’s highly competitive and dynamic marketplace.
Porter’s Generic Strategies are a foundational framework for businesses aiming to achieve a competitive edge in their industry. Developed by Michael Porter, this model outlines three key approaches: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Each strategy offers a distinct path for businesses to position themselves effectively against competitors. Companies that successfully adopt these strategies can improve market performance and create lasting value for their customers. Understanding how to apply Porter’s Generic Strategies is crucial for businesses looking to navigate today’s highly competitive and dynamic marketplace.
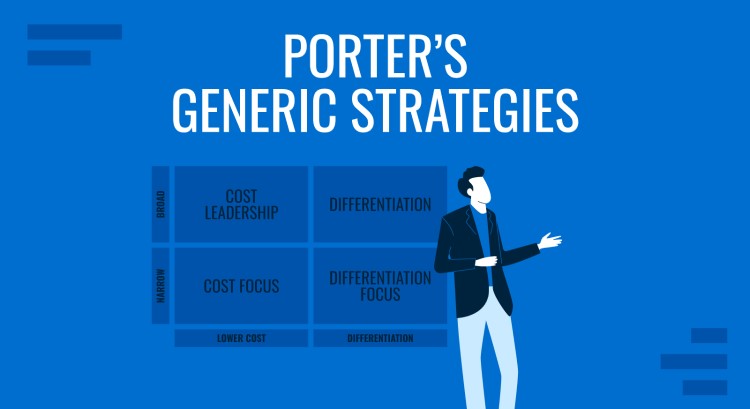
An Overview of Porter’s Generic Strategies
Porter’s Generic Strategies, developed by Michael Porter in 1980, are a widely recognized framework for gaining competitive advantage in any industry. Porter identified three primary strategies that businesses can use to outperform their competitors: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. These strategies are designed to help companies establish a strong position in the market and defend themselves against competitive forces. By adopting one of these approaches, businesses can effectively define their market position and attract their target audience.
Cost leadership focuses on being the lowest-cost producer, allowing companies to offer products at lower prices than competitors. Differentiation involves offering unique products or services, setting the business apart and allowing for premium pricing. The focus strategy, including cost focus and differentiation focus, targets niche markets where companies tailor offerings for smaller customer groups.
The significance of Porter’s Generic Strategies lies in their simplicity and versatility. Businesses of all sizes can adopt these strategies to establish a competitive edge in their respective markets. Whether a company seeks to become a low-cost leader or differentiate itself with unique offerings, Porter’s model provides a clear path for achieving sustainable success. By understanding and applying Porter’s Generic Strategies, businesses can effectively navigate competitive pressures and position themselves for long-term growth.
Cost Leadership Strategy
Cost leadership, one of Porter’s Generic Strategies, involves a business striving to become the lowest-cost producer in its industry. This strategy enables companies to offer products or services at lower prices than competitors, creating a competitive edge. By maintaining the lowest operational costs, businesses can either increase profit margins or undercut competitors, making their offerings more attractive to price-sensitive customers. This approach is particularly effective in markets where consumers prioritize price over unique features or brand loyalty.
One of the primary benefits of the cost leadership strategy is its ability to protect a company from competitive forces. Lower costs allow businesses to withstand pricing pressures and economic downturns more effectively. Additionally, cost leaders can maintain profitability even in highly competitive industries where margins are often tight. This strategy also creates barriers for new entrants, as it requires significant efficiency and scale to compete with established cost leaders.
To achieve cost leadership, businesses must optimize their operations, often through economies of scale, efficient production processes, and cost-saving innovations. This may involve automating key tasks, streamlining supply chains, or negotiating better deals with suppliers. However, cost leadership requires careful management to avoid sacrificing product quality or customer service. Companies that successfully adopt cost leadership within Porter’s Generic Strategies can create a durable competitive advantage, positioning themselves as resilient market leaders in price-sensitive industries.
Differentiation Strategy
Differentiation strategy, one of Porter’s Generic Strategies, involves businesses creating unique products or services that offer added value to customers. This strategy focuses on setting a company apart from its competitors by emphasizing distinct features, quality, innovation, or customer experience. Differentiation allows companies to charge a premium price, as customers are willing to pay more for products that provide exclusive benefits or superior quality.
One key advantage of the differentiation strategy is that it helps businesses build brand loyalty. Customers who perceive a product as unique or better suited to their needs are more likely to remain loyal, even if the price is higher. Differentiation also provides protection from competitors who may not be able to replicate the unique aspects of the offering. By focusing on innovation, design, or exceptional customer service, businesses can develop a strong competitive position that is difficult for rivals to challenge.
To successfully implement a differentiation strategy, companies must deeply understand their target market and consistently deliver the value customers expect. This often requires investing in research and development, marketing, or customer feedback to ensure products meet evolving demands. In addition, maintaining high standards of quality and continuously improving products is essential for sustaining a competitive advantage. By adopting the differentiation approach within Porter’s Generic Strategies, businesses can create a strong market presence and command higher profitability in markets where customers seek added value over low cost.
Focus Strategy: Cost Focus and Differentiation Focus
Focus strategy, one of Porter’s Generic Strategies, targets specific niche markets by concentrating on a particular customer segment or geographic area. This approach allows businesses to tailor their products and services to meet the unique needs of a smaller group of customers. Within this strategy, there are two distinct approaches: cost focus and differentiation focus. Both strategies enable companies to serve niche markets more effectively than broad competitors.
Cost focus involves delivering products at the lowest price within a specific market segment. Businesses pursuing this strategy aim to be the lowest-cost provider in a niche, offering affordable options to customers who are highly price-sensitive. Cost focus is particularly effective in markets where larger competitors overlook smaller segments due to lower profit potential. By maintaining low operational costs, companies can offer competitive pricing that appeals to a specific group while avoiding the need to compete across a broader market.
On the other hand, differentiation focus aims to provide unique, high-value products or services to a specialized segment. Businesses using this strategy offer tailored solutions that meet the particular needs of niche customers, often allowing them to charge premium prices. Differentiation focus works well when customers are willing to pay more for specialized products that address their unique preferences. This strategy can be effective in industries where customer demands are highly specific, such as luxury goods or specialized technologies.
Both focus strategies within Porter’s Generic Strategies can be highly effective when applied to niche markets. Companies that concentrate on specific customer needs, whether through cost or differentiation, can build strong market positions. This approach allows them to avoid direct competition with broader, more generalized companies and thrive by offering tailored value to their target segments.
Applications and Limitations of Porter’s Generic Strategies
Porter’s Generic Strategies provide businesses with a clear framework to gain competitive advantage. Companies can apply these strategies by choosing cost leadership, differentiation, or focus based on their strengths and market conditions. For example, businesses pursuing cost leadership must streamline operations and achieve economies of scale to offer lower prices. Differentiation strategies, on the other hand, require a deep understanding of customer needs to create unique offerings that provide added value. Focus strategies allow companies to specialize in niche markets, delivering tailored solutions that larger competitors may overlook.
However, while these strategies offer clear paths to competitive success, they also come with limitations. One key risk is being caught in the “middle,” where a business tries to adopt multiple strategies, such as pursuing both cost leadership and differentiation, and fails to succeed in either. This lack of focus can weaken a company’s position and confuse customers. Additionally, in today’s rapidly changing market, cost leadership strategies face challenges from technological advancements and global competition, making it harder to maintain a cost advantage. Companies that rely on differentiation must continuously innovate to stay ahead, as competitors can easily imitate their products or services.
To address these limitations, businesses should carefully evaluate their capabilities and market dynamics before choosing one of Porter’s Generic Strategies. Companies need to remain flexible and adapt their strategies as market conditions shift, ensuring they do not lose relevance. Understanding the potential risks and being prepared to evolve will help businesses effectively apply these strategies while navigating the complexities of modern competition. By focusing on their core strengths, businesses can still achieve a strong competitive edge in today’s challenging landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Porter’s Generic Strategies provide businesses with essential tools to gain and sustain a competitive advantage in various markets. Companies can tailor their approach through cost leadership, differentiation, or focus strategies to meet market conditions and customer needs. However, businesses must stay vigilant, as these strategies carry limitations and risks, like market shifts or competitors imitating products. By analyzing their strengths and the competitive landscape, businesses can effectively implement Porter’s Generic Strategies for long-term success.