The U.S. tax system includes federal, state, and local obligations, which can significantly impact your business. Tax treaties and incentives can offer relief, but only if you meet specific conditions. Planning your operations with these factors in mind helps you avoid costly mistakes.
This guide will help you understand key aspects of U.S. taxation, from filing requirements to tax-saving strategies. By staying informed, you can approach your tax responsibilities confidently and focus on growing your business.
Understanding the US Tax System for Foreign Entities
Navigating the U.S. tax system as a foreign entity involves understanding federal, state, and local tax obligations. At the federal level, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) taxes foreign companies on income effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business. Additionally, states and municipalities may impose their own taxes, which can vary significantly. Therefore, it’s important to research the specific tax requirements in each jurisdiction where you operate.
Domestic and foreign companies face different tax obligations in the U.S. While domestic corporations are taxed on their worldwide income, foreign companies are taxed only on income connected to U.S. activities. This distinction affects how you report income and calculate tax liabilities. Understanding these differences is essential for compliance and effective tax planning.
Tax treaties between the U.S. and other countries play a significant role in international taxation. These agreements aim to prevent double taxation and provide clarity on tax matters. By consulting the relevant tax treaty, you can determine how it impacts your tax obligations and identify potential benefits. This knowledge is valuable for managing your tax responsibilities effectively.
Tax Obligations for Foreign Companies Doing Business in the US
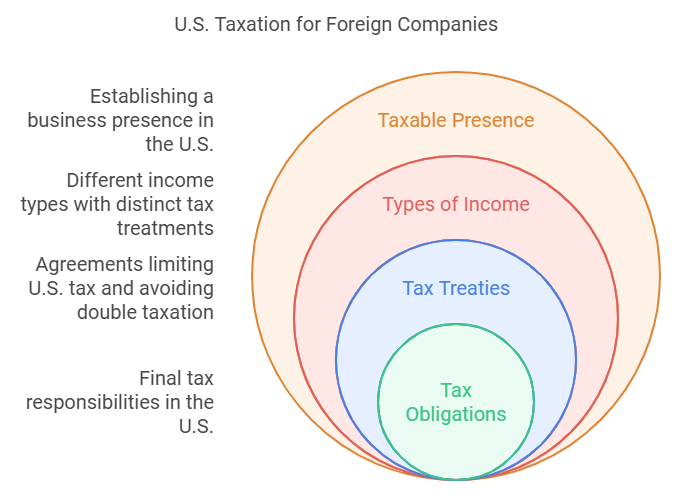
Establishing a taxable presence in the U.S. depends on specific criteria. One key factor is whether your business has a permanent establishment in the country. This could include having a fixed place of business, such as an office or a warehouse. If your company operates through agents or employees in the U.S., this can also trigger tax obligations.
Foreign companies are taxed on specific types of income derived from U.S. sources. Effectively connected income, or ECI, refers to income tied directly to a U.S. trade or business. This income is subject to regular corporate tax rates. Fixed or determinable annual or periodic income, such as dividends, interest, or royalties, is typically subject to withholding taxes. Understanding the differences between these income types helps you manage your tax liabilities.
Tax treaties play a significant role in shaping US taxation for foreign companies. These agreements can limit the U.S. tax on certain types of income and avoid double taxation. Treaties may also provide clarity on the definitions of permanent establishments and income classifications. Reviewing the relevant treaty between your country and the U.S. can significantly impact how you structure your business operations.
Corporate Tax Rates and Filing Requirements
The corporate tax rate in the U.S. for foreign companies is currently 21%. This rate applies to income effectively connected to a U.S. trade or business. Additional taxes, like withholding taxes on certain types of income, may also apply depending on the nature of the earnings.
If your foreign company operates in the U.S., you must file Form 1120-F to report taxable income. The filing deadline is generally April 15 for calendar-year taxpayers. Extensions are available, but you must submit the request by the original deadline. Filing requirements depend on the type of income and the extent of your business activities in the U.S.
Non-compliance with U.S. tax filing obligations can lead to significant penalties. If you fail to file Form 1120-F on time, you risk losing deductions and credits. Additionally, the IRS may impose financial penalties and interest on unpaid taxes. To avoid these issues, it’s important to understand and meet the requirements for US taxation for foreign companies.
Withholding Tax on Payments to Foreign Companies
Withholding tax applies to payments made to foreign companies for dividends, interest, royalties, and other income sourced in the U.S. These taxes are typically deducted at the source before payment. The standard withholding tax rate is often 30%, but the actual rate may vary based on specific agreements or exemptions.
Tax treaties between the U.S. and other countries can help reduce withholding tax rates. These agreements are designed to avoid double taxation and encourage international business. By applying the provisions of a treaty, you may qualify for lower rates or exemptions on certain types of income.
To claim reduced withholding rates, you must provide proper documentation, such as Form W-8BEN-E. This form certifies your eligibility for treaty benefits and helps avoid excessive tax deductions. Timely and accurate filing of this form is an essential part of managing US taxation for foreign companies.
Navigating Double Taxation and Tax Treaties
Double taxation occurs when foreign companies pay taxes on the same income in both the U.S. and their home countries. This can significantly increase your tax burden and reduce profits. Many foreign companies face challenges in managing this issue, especially when operating in multiple jurisdictions.
US tax treaties can help you avoid double taxation. These agreements define which country has the right to tax specific types of income. Treaties also often allow lower tax rates on dividends, interest, and royalties. By applying the terms of a treaty, you can align your operations to benefit from reduced tax obligations.
Foreign tax credits also play an important role in mitigating double taxation. If you pay taxes in one country, you may receive credit for those payments against your U.S. tax liability. This credit reduces the likelihood of being taxed twice on the same income. Understanding these mechanisms is essential to effectively manage US taxation for foreign companies.
Key Tax Incentives and Considerations for Foreign Investors
The U.S. offers various tax incentives to attract foreign companies. These incentives encourage investment and promote economic growth. Many states provide benefits such as tax credits, reduced rates, and exemptions for companies creating jobs or investing in local communities. Federal programs also offer opportunities for businesses in specific industries, like renewable energy or technology.
State-specific incentives can vary widely. Some states waive corporate income taxes for businesses in designated zones or provide property tax abatements for large-scale projects. Understanding these state-level options can help you reduce your overall tax burden. Researching incentives available in different regions is an important step when choosing where to establish operations.
Proper compliance and tax planning are essential for managing US taxation for foreign companies. Maintaining accurate records and understanding filing requirements can help you avoid penalties. Strategic planning, such as leveraging deductions and using applicable treaties, can optimize your tax liability. Working with experienced advisors ensures your operations align with U.S. tax laws while maximizing available benefits.
Conclusion
Understanding US taxation for foreign companies is essential for managing your business effectively and avoiding unnecessary costs. Tax obligations can vary widely depending on your operations and income types. By staying informed about tax rates, filing requirements, and available incentives, you can better plan your financial strategies.
Taking advantage of tax treaties and foreign tax credits helps you minimize double taxation and streamline your obligations. Compliance with federal, state, and local tax laws ensures smooth operations and reduces the risk of penalties. Seeking professional guidance can also help you navigate the complexities of U.S. taxation and optimize your tax position.
With the right planning and resources, you can successfully manage your U.S. tax responsibilities while maximizing the opportunities available for foreign companies. Staying proactive and informed allows you to focus on growing your business with fewer tax-related concerns.