Running a business means dealing with rules that affect nearly every decision you make. Business law covers those rules and helps you avoid legal problems. It touches everything from hiring and contracts to privacy and intellectual property. Therefore, knowing the basics gives you more control over your operations. You don’t need a legal degree, but you do need to stay informed.
Running a business means dealing with rules that affect nearly every decision you make. Business law covers those rules and helps you avoid legal problems. It touches everything from hiring and contracts to privacy and intellectual property. Therefore, knowing the basics gives you more control over your operations. You don’t need a legal degree, but you do need to stay informed.
Each legal area brings its own set of responsibilities. For example, employment laws affect how you hire and manage your team. Additionally, contracts must be clear and enforceable to protect your interests. If you run a digital business, privacy laws and intellectual property rights also come into play. These laws evolve often, so keeping up matters.
You may feel overwhelmed by the legal side of things. However, small steps go a long way. A strong contract or a proper business structure can save you time and money later. Therefore, think of legal knowledge as a business tool rather than a burden. It supports your growth and keeps you focused on your goals.
Additionally, handling legal risks early is more effective than reacting later. You don’t need to predict every problem. Instead, build habits that support good legal practices. That means reviewing your policies, tracking changes, and asking questions when things seem unclear. With the basics in place, you gain confidence in your decisions.
Forming a Legal Business Structure
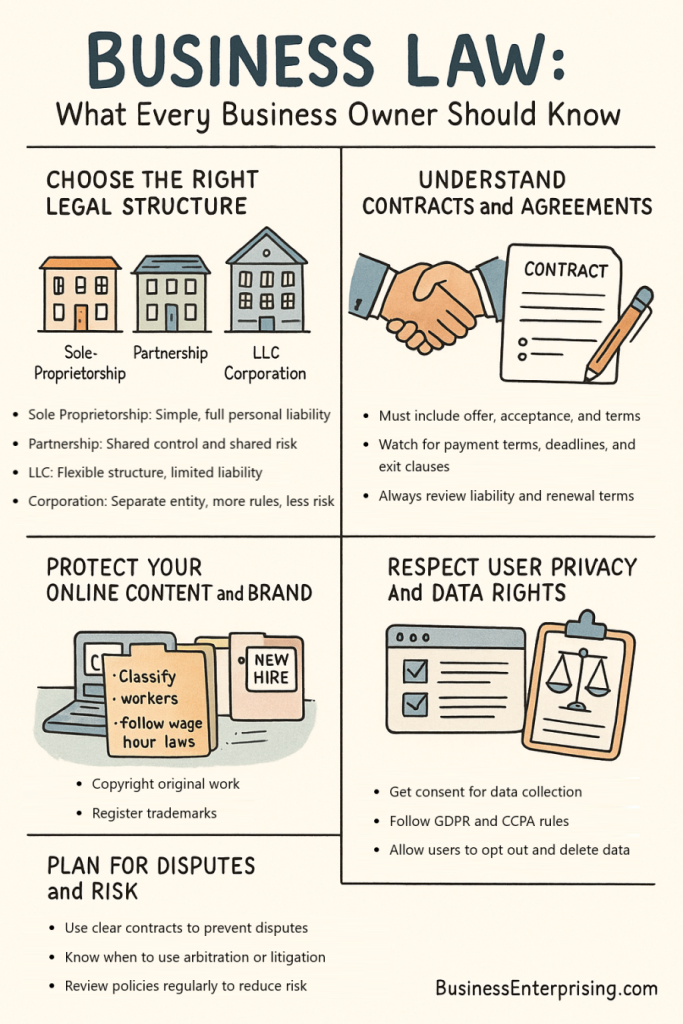
Choosing the right legal structure for your business affects how you operate, pay taxes, and handle liability. A sole proprietorship is the simplest option. You have full control, but you’re also personally liable for business debts. This setup requires little paperwork and typically uses your Social Security number for taxes.
A partnership involves two or more people who share ownership. It can be general or limited, depending on how you split liability and control. Additionally, profits pass through to each partner’s personal tax return. However, you may still face personal liability depending on the partnership type.
An LLC gives you liability protection without the complexity of a corporation. It separates your personal assets from the business, which helps reduce personal financial risk. Therefore, many small business owners choose this structure. LLCs also offer flexible tax treatment. You can be taxed as a sole proprietor, partnership, or corporation, depending on how you register.
A corporation is more complex but offers stronger protection. You create a separate legal entity that pays its own taxes. Additionally, shareholders are not personally liable for corporate debts. However, forming a corporation requires more paperwork and ongoing compliance.
Each structure has pros and cons, depending on your business goals. Before choosing, think about how much control you want, how you plan to grow, and what level of risk you can accept. Business law directly impacts how you form and manage these structures. Therefore, understanding each option helps you avoid mistakes and stay compliant as your business grows.
Navigating Contracts and Service Agreements
Understanding how contracts and service agreements work can help you avoid expensive mistakes. A legally binding contract includes an offer, acceptance, mutual understanding, and something of value exchanged. Each part matters, and skipping any can lead to disputes. Therefore, every agreement should be written clearly and reviewed with care before you sign.
Service agreements often outline the scope of work, payment terms, timelines, and responsibilities. Additionally, they should include how either party may terminate the agreement. Termination clauses help protect your business if things go wrong. They explain how to end the contract and what happens if that occurs.
Pay close attention to liability limitations. These sections define what each party is responsible for, especially if problems arise. Some agreements try to shift too much risk to one side. Therefore, you need to read the fine print and question anything that feels unbalanced. A service agreement should protect both parties equally.
Watch for auto-renewal terms, indemnification language, and vague performance metrics. These can all cause trouble later. Additionally, make sure the contract lists specific deadlines and deliverables. That way, you can hold others accountable if they fall short.
Business law helps define what makes a contract valid and enforceable. Understanding these basics puts you in a stronger position. Therefore, before signing any agreement, take time to review every section closely. If needed, you can ask questions or request edits. This protects your interests and helps build better business relationships.
Employment Law and Worker Classification
Understanding employment law starts with knowing the difference between an employee and an independent contractor. This classification affects taxes, benefits, and liability. Employees work under your direction and follow set schedules. Independent contractors work on their own terms and control how they complete tasks.
Misclassifying workers can lead to fines and legal trouble. Therefore, you need to evaluate the working relationship before hiring. Additionally, check for any local or federal rules that may apply to your business. Classification laws often vary by state, so staying aware is important.
You also need to follow wage and hour laws. These include rules on overtime, minimum wage, and required breaks. Therefore, make sure your pay practices meet the standards for each role. Additionally, you must keep accurate records for every employee. These include hours worked, rate of pay, and tax documents.
Many businesses also use non-compete agreements. These limit where and how a former employee can work after leaving your company. However, not all courts enforce these equally. Therefore, the agreement must be reasonable and clearly written. You should avoid broad terms that could be challenged later.
Workplace discrimination laws protect people based on race, gender, age, religion, and disability. These laws apply during hiring, training, promotion, and termination. Additionally, you must provide equal opportunities and address any complaints quickly. Business law sets the foundation for these practices and helps define what is legal. Knowing the rules and staying consistent reduces risk. It also creates a better work environment for your team and your company.
Copyright, Trademark, and IP Management for Online Content
Protecting your content starts with understanding how copyright and trademark laws apply to your business. If you create original work, you hold the copyright. This includes written content, images, videos, and graphics. Therefore, you should keep records that prove when you created the work. Additionally, you can register your copyright for stronger protection if needed.
Trademarks cover your business name, logo, and brand assets. These help you prevent others from using similar marks that might confuse your audience. Therefore, registering a trademark adds legal strength. It gives you the right to take action if someone tries to copy your brand. However, make sure your trademark doesn’t infringe on another company’s existing registration.
Intellectual property issues often come up when using content you didn’t create. You must respect others’ rights when sharing images, music, or code. Additionally, review licenses before using third-party assets. Some licenses allow commercial use, while others have limits. Therefore, always check the terms before posting or distributing content.
Digital businesses must also comply with the DMCA. This law protects copyright holders and outlines how to handle infringement claims. If someone uses your content without permission, you can file a takedown request. However, you must follow the proper steps and provide specific details.
Business law covers how you protect your ideas and how you use others’ work. Taking these rules seriously helps you avoid conflict and protects your brand long term. Therefore, set clear guidelines for your team when publishing anything online.
GDPR, CCPA, and Privacy Compliance for Digital Platforms
If your business collects user data, you must follow privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. These laws focus on how you collect, store, and use personal information. GDPR applies to users in the EU. CCPA applies to residents of California. Both give people more control over their data and how it’s used.
You need to explain what data you collect and why you collect it. Additionally, you must give users the choice to opt in or out. Consent management is a key part of staying compliant. Therefore, your website should include clear consent forms and easy opt-out options. Make sure users can change their preferences at any time.
User rights include the ability to access, correct, or delete personal data. Additionally, users may request that you stop sharing their information. You must respond to these requests in a timely manner. Therefore, your team should have a system in place to track and process privacy-related requests.
Each law has its own requirements, and they change depending on location. However, you can build a standard process to manage compliance. Use simple language in your privacy policy. Train your staff on data handling and update your tools to support legal standards. These steps reduce your risk of penalties and build user trust.
Business law covers how digital platforms manage user data. Therefore, staying compliant is not only a legal requirement but also a smart business move. When you treat privacy seriously, you protect both your customers and your brand.
Dispute Resolution and Legal Risk Mitigation
Business disputes happen, even when you plan carefully. These may involve clients, vendors, employees, or partners. Therefore, knowing how to handle them helps protect your business. Start by reviewing the terms of any contracts involved. Additionally, keep communication clear and documented throughout the process.
You have a few ways to resolve disputes. Litigation happens in court and can be time-consuming and expensive. However, it may be necessary when one party refuses to cooperate. Arbitration is faster and usually private. It involves a neutral third party who makes a decision after hearing both sides. Therefore, some businesses prefer it to avoid drawn-out court battles.
Each method has benefits and drawbacks. Litigation allows appeals but can damage relationships. Arbitration moves quickly but rarely allows for appeal. Additionally, many contracts include mandatory arbitration clauses. You should review these carefully before signing any agreement.
To reduce legal risks, write clear contracts and follow written policies. Additionally, train your team to handle disputes calmly and professionally. Set up internal procedures for dealing with complaints. These steps may help you avoid legal action altogether. Therefore, being proactive is often less costly than waiting until something goes wrong.
Business law outlines the rules for dispute resolution and risk management. You don’t need to be a lawyer, but you should understand the basics. That knowledge helps you make smart decisions and protect your company from future problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of business law helps you make informed decisions and avoid costly problems. Each topic discussed above affects how you run and protect your business. Therefore, learning the essentials is more than a good practice. It supports long-term success.
Additionally, laws can vary by location, so it’s important to stay informed as your business grows. Contracts, hiring practices, and online content all carry legal risk. However, with clear systems in place, you can reduce that risk and operate with more confidence. Many legal issues are preventable with a little planning upfront.
You don’t need to become an expert to make better legal choices. Instead, focus on building habits that support compliance and documentation. Additionally, review your policies and agreements often. This keeps your business updated and reduces surprises down the road.
Therefore, take time to think about how each legal topic connects to your day-to-day operations. Whether it involves employees, clients, or digital platforms, laws apply across all areas of business. Additionally, make it easy for your team to follow those rules with clear processes.
Business law provides the structure you need to run responsibly and protect your interests. With a little effort, you can handle the basics and avoid bigger issues. If something feels unclear, ask questions and get help before a problem grows. Taking action early often makes all the difference.